Air pollution contributes to health and environmental problems!
Air pollution began as a byproduct of the Industrial Revolution with waste from industrial facilities like factories. Polluting industries need to follow policies to protect public health.
Most air pollution is created by people, including factory emissions, aerosol cans, planes, and vehicles. Second-hand cigarette smoke is also considered air pollution.
Air pollution contributes to climate change because smog is intensified by heat caused by climate change and produces more ultraviolet radiation.
Fossil fuels release life-threatening air pollution and are also involved in producing greenhouse gases that intensify climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions need to be reduced to help those affected by air pollution to breathe clean air and avoid infectious diseases, global warming, increasing ozone levels, and to save the earth.
Top 10 Most Horrifying Air Pollution Facts
- Air pollution is one of the major environmental risk and health hazard
- Annually, 6.7 million early deaths are attributed to air pollution
- 9 out of 10 people on planet are breathing in polluted air
- Almost 93% of children live in areas where air pollution surpasses WHO guidelines
- Tiny PM2.5 pollutants can breach protective barriers of human body
- Air pollution carries an economic burden of almost $3 trillion
- Burning of fossil fuels is a major reason behind air pollution
- India hosts 10 out of the world’s 15 most polluted cities (IQ Air)
- Adhering to the ‘Paris Agreement’ goal of limiting global warming to 2°C can save a million lives
- Enhancing cleaner transport, and proper waste management, can mitigate air pollution
Air Pollution Facts
Brace yourself for eye-opening air pollution insights that prompt reflection and action:

Air Pollution Is One of the Major Environmental Risks and Health Hazards (WHO)
Most air pollution is manmade, but a couple of natural sources are wildfires and sea salt.
1 in 10 people die from air pollution-related illness, and air pollution is a leading risk factor in chronic health diseases and early death rates around the world. In 2017, air pollution caused an estimated 5 million people to die globally, which is 9% of the world’s population.
Air Pollution Is the Second Highest Risk of Noncommunicable Diseases (WHO)

Air pollution causes people to catch noncommunicable diseases. The health effects of air pollution are staggering. One-third of deaths from heart issues, stroke, and lung cancer, can be traced back to air pollution. Exercising outside is dangerous to your health in polluted areas.
The five countries with the worst polluted air are located in Asia, and air pollution is increasing in Central and West Africa, where average life expectancy has dropped by two to six years. Now air pollution is a greater threat to more people’s lives than HIV/AIDS, smoking, war, and malaria. Poor air quality is literally killing millions of people around the world.
Annually, 6.7 Million Early Deaths Are Attributed to the Combined Influence of Both Outdoor and Indoor Air Pollution (WHO)
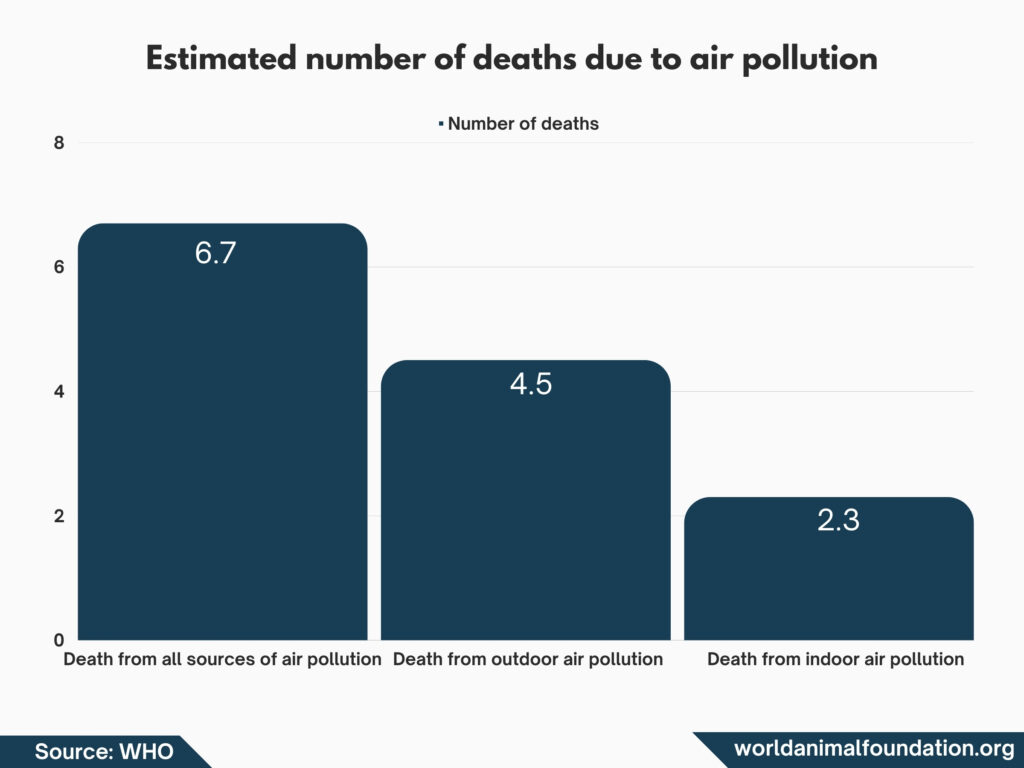
The combined effects of outdoor air pollution and household have such an enormous impact that each year air pollution is associated with 6.7 million people dying prematurely annually.
Indoor air pollution (often from cooking) can cause noncommunicable illnesses, including stroke, malignant tumor in the lungs, respiratory disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and Ischaemic heart diseases.
Approximately Outdoor Air Pollution Caused 4.2 Million Deaths Back in 2019 (WHO)
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), ambient air pollution is outside air pollution that occurs when pollutants reach “high enough concentrations to affect human health and/or the environment” and exists in cities.
89% of These Premature Deaths Occurred in Low and Middle-Income Countries (WHO)
WHO reports that Southeast Asia and Western Pacific Regions are areas where pollution-related premature deaths are highest. Deadly ailments linked to air pollution are cardiovascular illnesses. Middle-income countries are also in danger.
Smog and Soot Are the Two Most Prevalent Forms of Air Pollution (NRDC)

New research found that fine particulate matter (soot) is more harmful than thought before. Approximately 8.7 million people a year die early due to coal, burning gasoline, and oil. That’s 20% of global deaths. The new research about pollutants shows that the fossil fuels driving climate change are quite deadly.
The US established the Clean Air Act in 1970 to protect the environment. It’s part of the Natural Resources Defense Council’s (NRDC) Climate and Clean Energy program. The Clean Air Act aims to reduce burning fossil fuels because that releases gases and chemicals into the air, contributing to climate change.
The plan is supposed to reduce about 80 billion tons of carbon dioxide during the next 35 years and move us toward pollution free. Improvements have already been reported by countries around the world.
Air Pollution Is Also Destroying the Health of the Planet by Inducing Climate Change (WHO)
Smog, which is intensified by increased heat–a byproduct of climate change, creates ultraviolet radiation. Carbon dioxide and methane raise the earth’s temperature. Climate change also increases the production of main air pollutants, including mold–a result of dampness from extreme weather and increased flooding and pollens. Pollen season has increased because of greenhouse gases.
When homes, schools, or businesses have water damage, mold can grow, and it can produce allergens/ airborne pollutants. Some molds produce toxins.
Particulate Matter (PM), Ozone (O3), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), and Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Are the Major Pollutants in the Air (WHO)

Air pollutants like particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide (CO), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2) are the most harmful pollutants to our health. Health issues occur from short- and long-term exposure to them.
For some pollutants, even the smallest exposure leads to illnesses. Nitrogen can affect your lungs and make you vulnerable to bronchitis and respiratory disease.
Tiny PM2.5 Pollutants Can Breach Protective Barriers in Our Bodies, Damaging Lungs, Heart, and Brain (WHO)
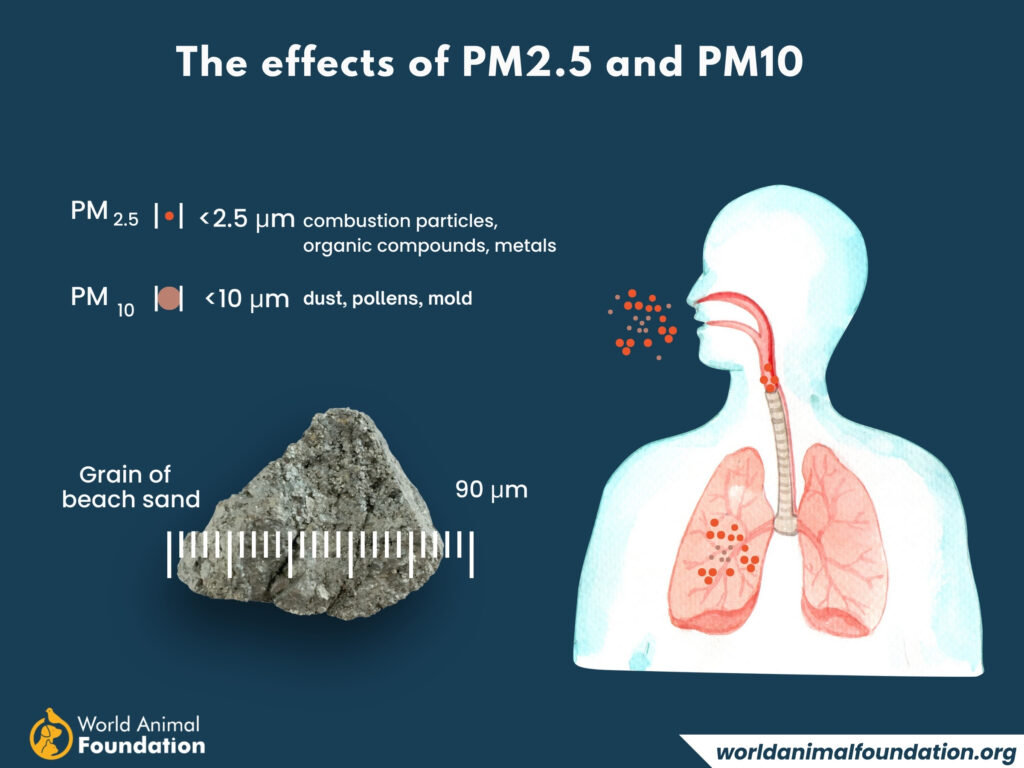
Fine particles are able to penetrate deeply into our lungs (causing respiratory disease) and possibly into our bloodstream, where they can cause lots of harm, making particulate matter (PM) very dangerous.
Studies have linked PM to decreased lung function, nonfatal heart attacks, irritation of the airways, difficulty breathing, coughing, irregular heartbeat, aggravated breathing issues, premature deaths in people with heart or lung disease, and decreased lung function.
Approximately 25% of Urban Fine Particulate Matter Air Pollution Comes From Traffic, While Domestic Fuel Burning and Industrial Operations Contribute Around 20% and 15%, Respectively (NIH)
A recent study showed that globally 25% of urban ambient PM2.5 is generated by traffic, 15% by industrial activities, 20% by domestic fuel burning, 22% from unspecified sources of human origin, and 18% from dust and salt.
The most vulnerable populations to air pollution are those with heart or lung diseases; children and older adults are highly susceptible. Click on AirNow to check air quality near you because you may not see pollution, so you know when to avoid poor air quality and polluted air.
Air Pollution Carries an Economic Burden of Almost $3 Trillion, Equivalent to 3.3% of the Global GDP (Energy and Clean Air)
In addition to protecting ourselves from the health hazards of air pollution, by reducing it, we can save practically $2.9 trillion.
There Lies a Positive Correlation Between Air Pollution and the Spread of COVID (Medrvix.org)
A study in the Netherlands indicated that exposure to fine particulate matter increased COVID-19 incidence in 355 municipalities in the Netherlands, showing how serious the effects of air pollution caused by particulate pollution are.
Burning Fossil Fuels Is a Major Reason Behind Different Environmental Crises, Including Air Pollution (WHO)

Airborne nitrogen impacts air, land, and water quality negatively. Nitrogen is the most abundant element in the air and is essential to plant and animal life. Nitrogen is increased by human activities like agriculture, industry, electricity, power generation, and road traffic, and it can ruin the natural balance of nitrogen in the environment.
Burning fossil fuels for road traffic causes the release of nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere, which produces smog and acid rain. The most common human-caused nitrogen-related compounds are nitrogen oxides.
Agricultural activities cause ammonia, another nitrogen compound, to be released. Ammonia can also come from burning fossil fuels. Transportation and industry are the two main nitrogen culprits.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) are emitted from vehicle exhausts and can cause liver health problems. Major sources of nitrogen oxide emissions include:
- Vehicles
- Coal-fired power plant (burning fossil fuels) emissions
- Large industrial operations emissions
- Ships and airplanes’ fuel emissions
Enhancing Cleaner Transport, Energy-Efficient Homes, and Proper Waste Management Can Substantially Mitigate Outdoor and Indoor Air Pollution (Science Direct)
Fortunately, there are mitigations that will help protect us from and reduce air pollutants and their impact on our health.

- Open windows
- Ban smoking
- Bathe your pets (they are dander machines)
- Use exhaust fans while cooking
- When stuck in heavy traffic, use the recycled-air setting on your fan so your car doesn’t take in harmful fumes.
- Use a doormat
- Wipe shoes or don’t wear them in the house
- Change Filters
- Don’t light fireplace fires because they release soot and smoke(like wildfires)
- Don’t use air fresheners, incense, or scented candles
- Vacuum often
- A microfiber dusting clothcollects dirt effectively
- Minimize carpeting to avoid dust mites, dander, dirt, mold spores, etc.
- Use a dehumidifier to reduce mold and clean the filter
- Store chemicals safely and use white vinegar and water instead chemical-filled commercial cleaners
- Buy an air purifier
- Use public transportation
Air Pollution Statistics

Explore the figures that reveal the extent of the challenge we face, urging us to take collective action for cleaner air and a healthier world:
9 out of 10 People on Our Planet Are Breathing Polluted Air (WHO)
Recent estimates bring forward a startling reality: each year, 7 million lives are claimed by outdoor and indoor air pollution combined. Air pollution puts us all at risk, but its harshest impact falls on the most vulnerable and marginalized communities, amplifying the inequality we must address.
It’s Estimated That Almost 800 People Get Killed by Air Pollution Each Hour (UNEP)
Every year, a heartbreaking 600,000 children lose their lives due to dirty air. And that’s not all – breathing in polluted air also affects their brain development, causing cognitive and motor difficulties. This puts them at higher risk for chronic illnesses in the future.
Almost 93% of Children Worldwide Reside in Areas Where Air Pollution Surpasses WHO Guidelines (WHO)
Air pollution poses a significant risk to children’s health, contributing to nearly 1 in 10 deaths among kids under five years old.
Deaths Caused by Air Pollution (WHO)
Air pollution claims lives at an alarming rate, according to WHO data:
- 43% of deaths from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- 29% from lung cancer
- 26% of deaths from ischemic heart disease
- 24% of deaths from strokes
According to The American Lung Association, More Than 40% of the US Population Is at a Higher Risk of Premature Deaths Due to Air Pollution. (American Lung Association)
Many premature deaths can be avoided by reducing airborne particles and using cleaner fuels, especially in developing countries and some middle-income countries, where people are most affected by air pollution.
WHO Minimum Air Quality Levels Are Not Achieved in 97% of Cities in Low- and Middle-Income Countries With Over 100,000 Residents (UNEP)
Household air pollution rates are higher in low and middle-income nations that use solid fuels like charcoal and coal, wood, and crop wastes, plus kerosene in open fires for cooking.
India Has 10 of the World’s 15 Most Polluted Cities, Including Delhi. (IQ Air)

Decreasing pollution levels can increase life expectancy. Residents in India, which suffers from very severe air pollution, could add 5.9 years to their lives rather than suffering from premature deaths.
According to Stats for 2022, Lahore Had a 97.4 PM 2.5 Particulate Concentration and Was the Most Polluted City in the World (Statista)
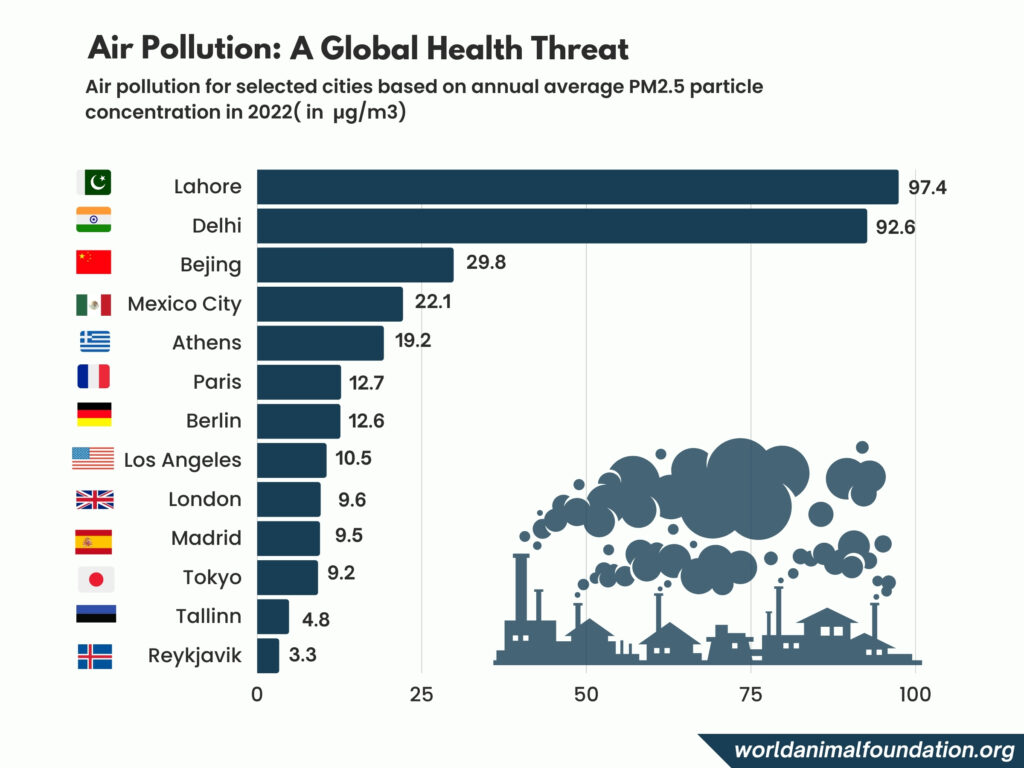
Four countries that have almost a quarter of the world’s population are also among the most polluted: Bangladesh, India, Nepal, and Pakistan.
Other countries are also experiencing untimely deaths. Air pollution causes over 1,200 premature deaths per year in people under 18 in Europe and increases the chance of disease later in life.
Meeting the ‘Paris Agreement’ Goal of Limiting Global Warming to 2°C Could Potentially Save the Lives of a Million People Annually by 2050 by Decreasing Air Pollution (WHO)
Air pollution causes serious health problems. By reducing air pollution levels, countries can decrease strokes, heart issues, diabetes, malignant lung tumors, and chronic and acute respiratory problems. Polluted air can also affect people’s nerves, liver, kidneys, liver, brain, and other organs and trigger asthma attacks.
Air Pollution’s Health Toll in the 15 Largest Greenhouse Gas Emitters Exceeds 4% of GDP (WHO)
Air pollution claims 7 million lives yearly and has economic costs of a staggering $5.11 trillion worldwide. The top 15 emission countries face over 4% of GDP in health-related expenses. Research by MIT showed that approximately 13,000 British citizens die from pollution from power plants and vehicles in Europe.
Siberia experienced horrible wildfires, and smog reached dangerously high levels, forcing more than 280,000 residents to stay in their homes.
China Has Achieved a 29% Reduction in Particulate Pollution Within Six Years (EPIC)
Kudos to China for investing more in solar energy than any other country–nearly half of all global investment. China has achieved a 29% reduction in particulate pollution within six years.
Causes of Air Pollution

Air pollution is created when liquid and solid particles–called aerosols–and certain gases are suspended in the air. They can come from wildfires, mold spores, vehicle exhaust, factories, pollen, and volcanoes.
Carbon dioxide causes 81 percent of greenhouse gas emissions, while methane accounts for approximately 11 percent.
Measures to Stop Air Pollution
NRDC’s Climate and Clean Air program estimates that they can make a hydrofluorocarbon phase-down that would help reduce about 80 billion tons of carbon dioxide over the period of the next 35 years. Public health is in danger, and premature death rates need to be eliminated. You can reduce air pollution by:
- Driving your car less
- Making sure your car isn’t producing excessive exhaust, and keeping your car tires inflated to optimize gasoline mileage
- Turning off your engine because idling = pollution
- Not burning your garbage
- Limiting backyards fires
- Only burning dry firewood
- Not building campfires during an air quality alert
- Planting and caring for trees
- Switching to electric or hand-powered lawn equipment
- Using efficient appliances and heating systems and turning off electrical items you’re not using
- Use solar, electric, biogas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), natural gas, alcohol fuels, and biomass stoves for cooking.
- Use an exhaust fan while cooking inside
FAQs
How Does Air Pollution Affect the Environment?
Air pollution can contaminate the surface of bodies of water and soil, killing crops or reducing their produce. Plants and young trees can die from pollution.
Acid rain is created by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide in the atmosphere when they mix with water and oxygen in the atmosphere. Coal-fired power plants and motor vehicles are responsible for acid rain, which damages plants by changing soil composition, damages crops, makes buildings and monuments decay, and affects the quality of water in streams, lakes, and rivers.
Air pollution can cause disease, birth defects, and lower reproductive rates in animals.
What Are Types of Air Pollution?
Types of air pollution include:
1. Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5): Composed of tiny particles, they harm the brain, lungs, and heart, and PM2.5 can speed up brain aging.
2. Ground-level Ozone (O3): A component of smog from vehicle emissions and industry, worsened by household equipment, calls for reduced car pollution.
3. Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): From combustion in power, heating, transport, and diesel engines, causing respiratory diseases and exceeding limits.
4. Carbon Monoxide (CO): Comes from incomplete fuel combustion in vehicles and homes, affecting breathing and tissues and even causing death.
5. Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): Emitted from fossil fuel burning, linked to ER visits and respiratory issues, particularly impacting those with existing conditions.
Where in the US Is There More Air Pollution?
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reported that about 68 million tons of air pollution were emitted into the atmosphere in the US in 2020.
The American Lung Association named 11 counties in California and one in Arizona as having the most industrial facilities and worst polluted areas in the US. They received bad grades for ozone and short-term and year-round pollution: Fresno, Kern, Kings, Los Angeles, Madera, Riverside, San Bernardino, Stanislaus, Sutter, and Tulare in California, and Pinal in Arizona have the most polluted cities.
What Human Activity Contributes to Air Pollution?
Human beings contribute to air pollution from vehicles burning coal, oil, and manufacturing chemicals. Even filling your car with gasoline, dry cleaning, and degreasing and painting operations generate air pollution. Because the pollution is human-caused, we can reduce air pollution by stopping and/or decreasing practices that cause it.
Which Type of Pollution Includes CFCs and Smog?
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are compounds used as solvents, refrigerants, and propellants. The most common sources of chlorofluorocarbons are aerosols and leakages from refrigeration equipment.
What Is a Possible Long-Term Effect of Continued Exposure to Air Pollution?
A potential effect of long-term exposure to air pollution is an increased risk of chronic health conditions such as respiratory diseases (e.g., asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), cardiovascular issues, and even certain types of cancer.
Prolonged exposure to pollutants can also contribute to the deterioration of lung function, cognitive decline, and reduced overall quality of life. Air pollution problems can also result in increasing climate change and causing the extinction of animals and plants.
Conclusion
As we confront these stark air pollution facts, the path ahead becomes clearer – to safeguard our planet and our health, we must unite in the pursuit of cleaner air, sustainable practices, and a future where every breath is a testament to our commitment to a healthier world.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Please feel free to comment and/or share.


