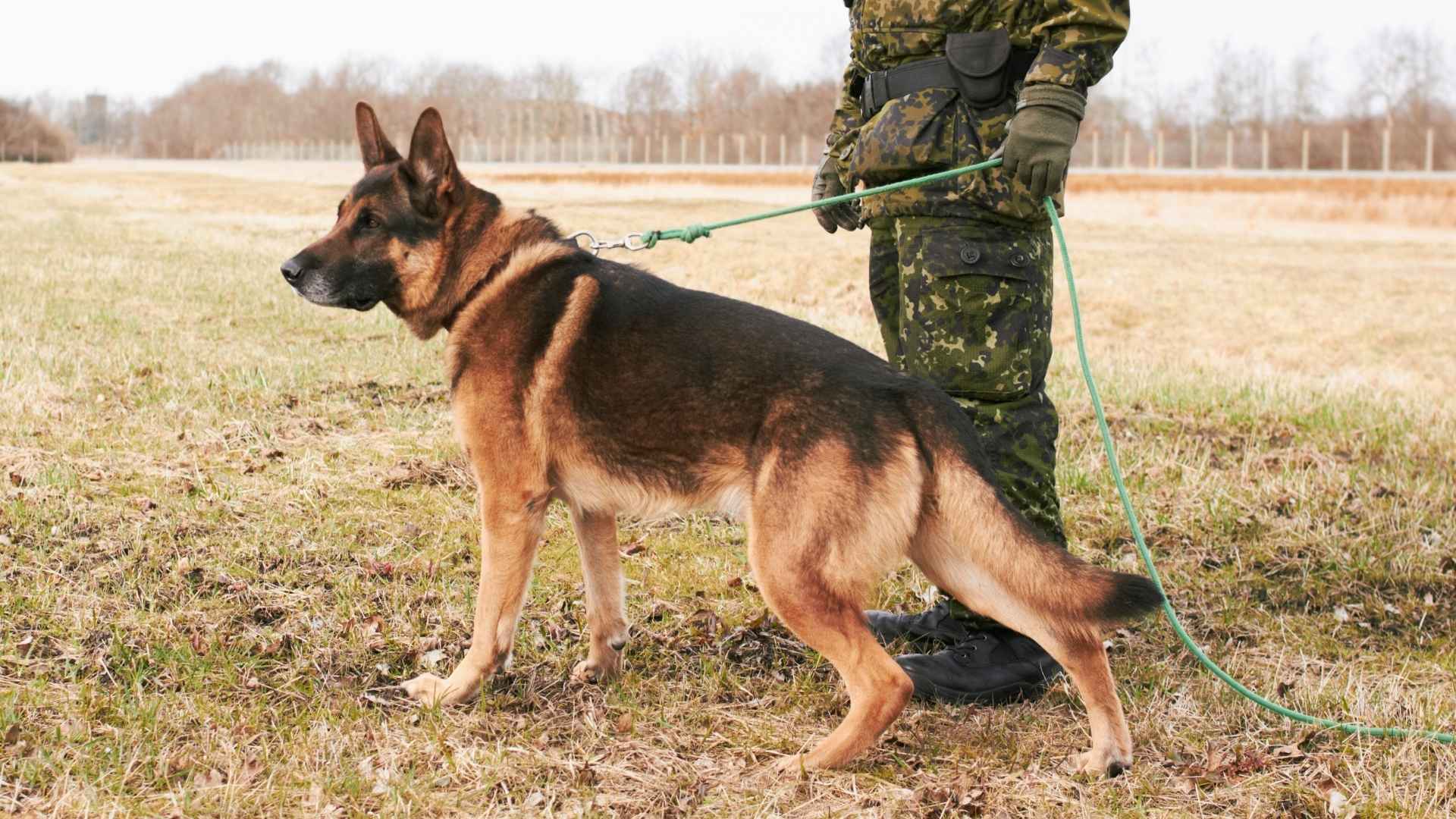
For centuries, dogs have stood beside soldiers in battle, fierce, focused, and fiercely loyal. These military canines are more than just companions; they are trained operatives with the instinct and intelligence to carry out high-risk missions. From ancient warfare in 600 B.C. to modern-day special forces operations, dogs have played a crucial role in shaping military history.
Whether tracking enemies, detecting hidden explosives, or calming nerves during intense operations, these dogs are indispensable assets on the battlefield. The world saw just how vital they are in 2019, when Conan, a Belgian Malinois, earned national praise for his role in a U.S. Special Forces raid against ISIS leader Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi. His valor highlighted the silent but powerful contributions that working dogs bring to modern warfare.
Over time, various dog breeds have proven their worth on the front lines, each chosen for their unique blend of courage, endurance, and unwavering loyalty.
US Military Dog Breeds
1. German Shepherd
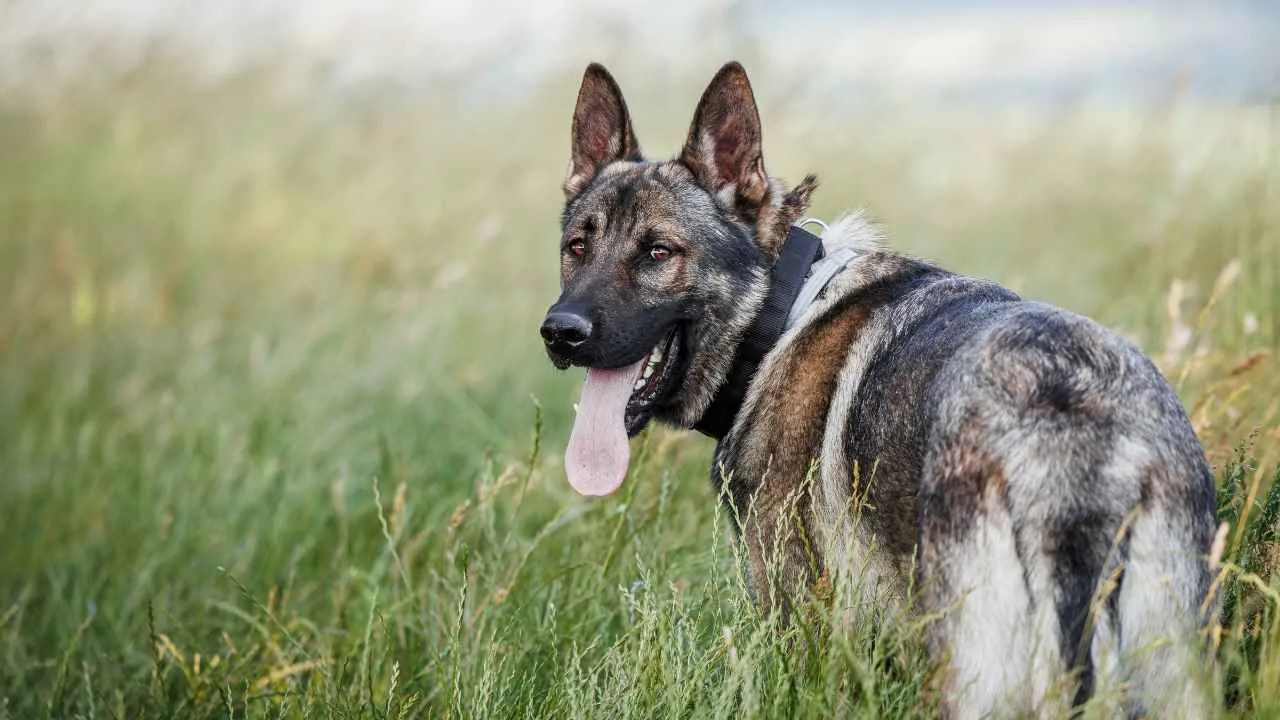

The German Shepherd is the quintessential U.S. military dog, revered for its unmatched combination of intelligence, agility, and adaptability. The AKC describes the German Shepherd Dog as a noble and versatile breed, known for being a large, strong, and agile all-purpose working dog.
This is one of the top military dog breeds. Whether navigating combat zones, detecting explosives, or serving in peacekeeping operations, these dogs are indispensable to military missions.
Their discipline and mental sharpness enable them to perform under pressure, while their calm demeanor ensures they can also provide emotional support and work closely with civilians and fellow soldiers alike.

History
Originally developed in Germany in the late 1800s, the breed was refined by Captain Max von Stephanitz, who sought to create the ultimate herding dog. He achieved this by crossbreeding dogs from various German regions, leading to the birth of the modern German Shepherd.
Their talent quickly shifted from herding to service work, gaining popularity in the U.S. during the early 1900s. By both World Wars, the breed was deployed as messengers, guards, and supply carriers. Today, German Shepherds remain a top choice for military and police forces worldwide.
Fact: The German Shepherd is the most commonly used breed in the U.S. military, with their skills spanning everything from bomb detection to therapy support roles.
2. Belgian Malinois
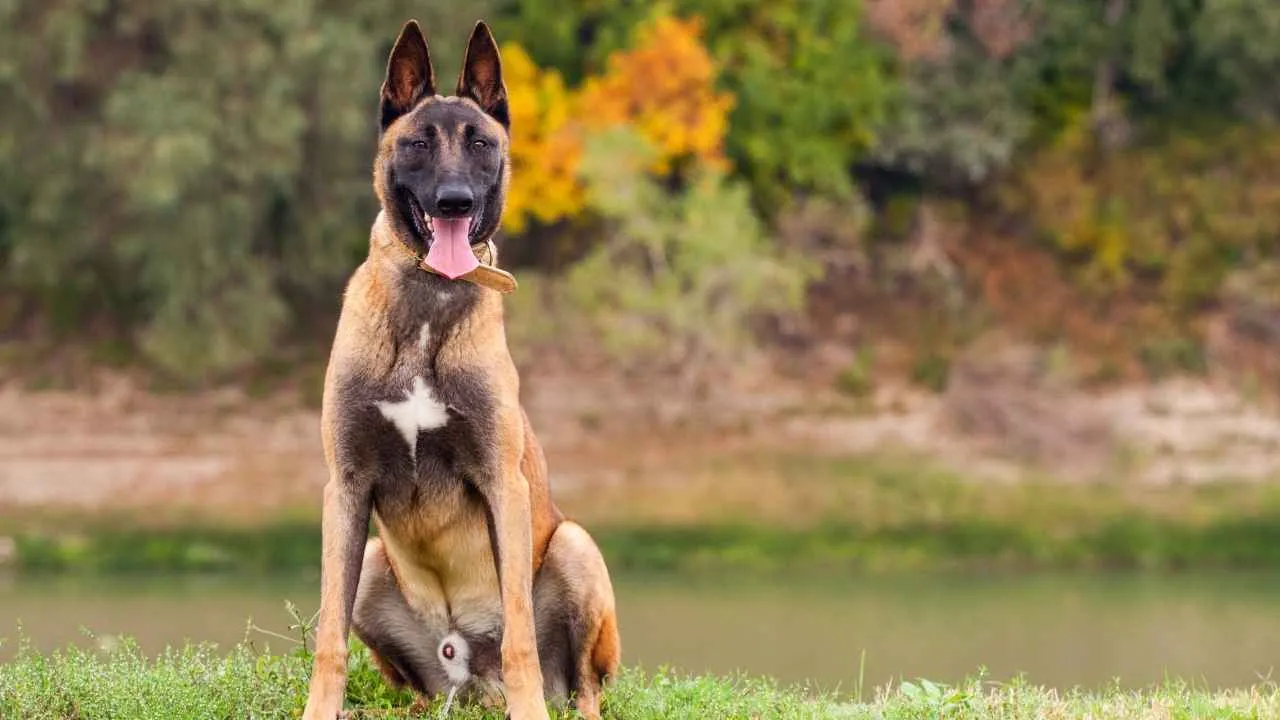

The Belgian Malinois is recognized for its unmatched speed, intelligence, and unwavering focus. Their nimble build, intense drive, and exceptional loyalty make them ideal for high-risk operations, such as scouting, detection, and airborne missions.
Unlike some larger breeds, their agility allows them to maneuver swiftly through tight spaces, rappel with handlers, and deploy via parachute when necessary. PetMD states that the Belgian Malinois is among the most self-assured, intelligent, and diligent of all dog breeds.

History
Originating near the city of Malines in Belgium, this breed was initially developed for herding. Over time, their work ethic and responsiveness to training led them into various service roles.
As one of the four varieties of Belgian Shepherds, the Malinois quickly earned a reputation beyond the pasture. They became essential in police work, search and rescue, and narcotics detection.
Their military rise was propelled by their physical endurance and quick reaction time, earning them positions in elite units, including Navy SEAL teams.
Fact: A Belgian Malinois was famously part of the U.S. Navy SEAL team that executed the raid on Osama Bin Laden’s compound, showcasing the breed’s capability in elite military operations.
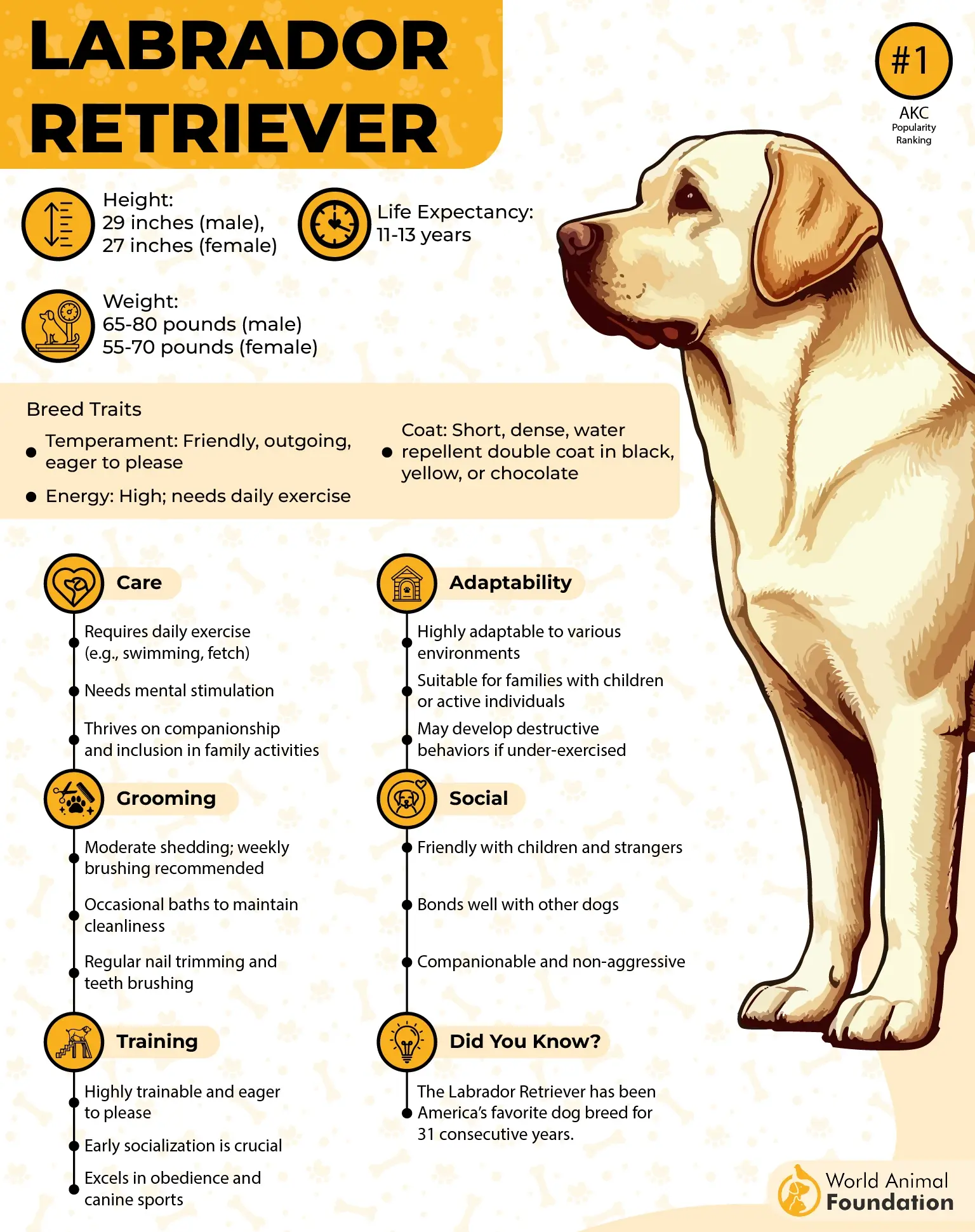
3. Labrador Retriever
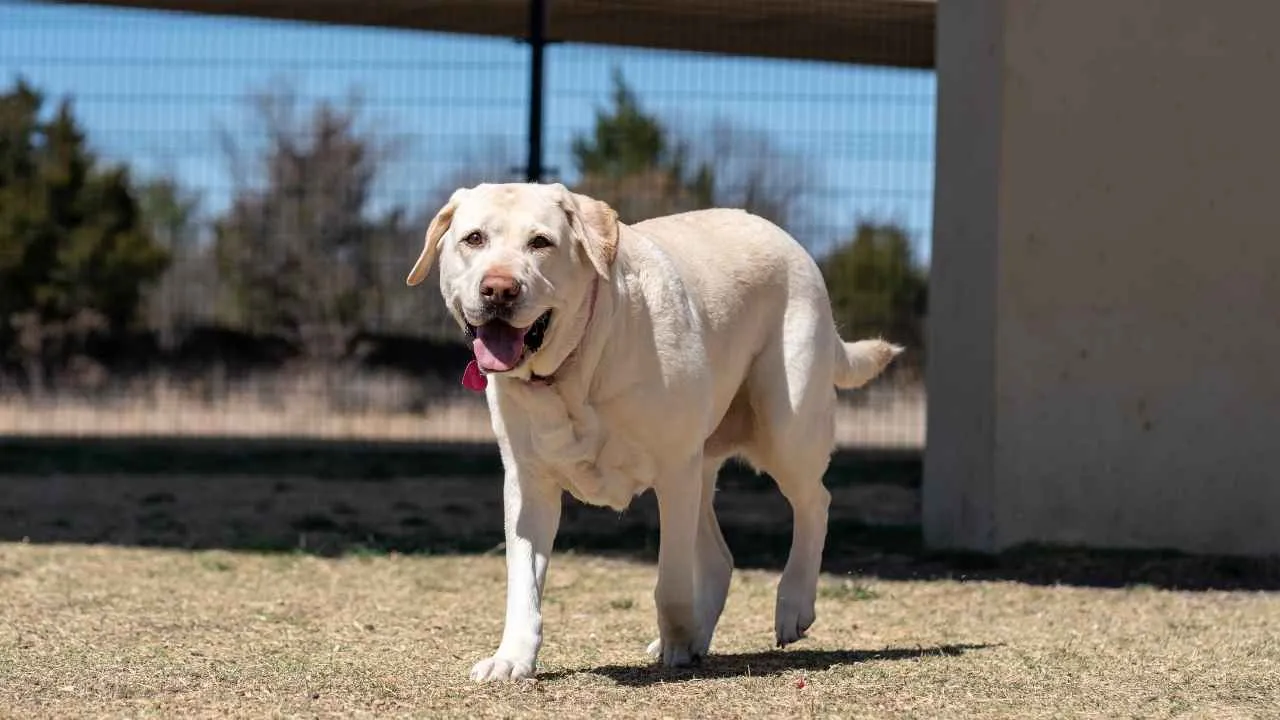

The Labrador Retriever has unmatched scent detection and a composed nature. Purina describes Labradors as robust, well-built dogs with strong frames. They have broad heads and gentle, intelligent eyes that reflect their friendly and easygoing temperament.
During missions, these dogs demonstrate precision and steadiness, whether sniffing out hidden explosives, tracking enemy movements, or aiding in the recovery of injured personnel.
Their even temperament also makes them ideal canine companions in emotionally charged combat zones, providing reassurance and morale boosts to troops in high-stress environments.
History
Though the name suggests otherwise, the Labrador Retriever originated on the coast of Newfoundland in the 17th century, where they helped fishermen haul in nets from icy waters.

In the 1800s, the breed gained popularity in Great Britain as working gundogs, largely due to the Earl of Malmesbury’s breeding efforts. Known for their eagerness to please and strong work ethic, Labs became a staple in military operations by the Vietnam War.
Deployed to track enemy soldiers and locate missing airmen, they were often embedded with small combat teams in dense jungle terrain. In modern deployments across Iraq and Afghanistan, they continue to serve heroically as explosive-detection dogs.
Fact: Labrador Retrievers were the U.S. military’s first choice for combat tracking during the Vietnam War due to their keen noses and reliable temperament.
4. Dutch Shepherd
The Dutch Shepherd is admired for its unmatched adaptability, intelligence, and work ethic. These dogs are quick to learn, eager to serve, and physically robust, traits that make them ideal for demanding military tasks such as scent detection, extended patrols, and high-agility missions.
While they may not yet be as widely recognized as German Shepherds or Belgian Malinois, Dutch Shepherds are every bit as capable on the front lines. Their ability to operate independently while maintaining loyalty to their handler sets them apart in high-pressure environments.
History
Bred originally in the Netherlands during the 19th century, Dutch Shepherds were designed to be versatile farm helpers. Their herding instinct, guarding ability, and even cart-pulling strength made them invaluable in agricultural communities.
Known also as “Dutch Herders,” they were officially standardized in 1898, and by 1914, only brindle-colored coats were recognized to differentiate them from their German and Belgian counterparts. Today, their heritage of resilience and versatility continues to serve them well in military settings.
Fact: Dutch Shepherds, alongside German Shepherds and Belgian Malinois, are among the top three breeds currently employed by the U.S. military for patrol and explosive detection roles.
5. Doberman Pinscher
The Doberman Pinscher is a big, active breed that needs daily mental and physical stimulation, such as a brisk jog or intense playtime for at least an hour each day, as per Britannica.
Elegant yet commanding, the Doberman Pinscher is a breed synonymous with courage, loyalty, and swift precision, qualities that made it a valuable asset to the U.S. military, particularly during the World Wars.

Renowned for its trainability and innate guarding instincts, the Doberman proved highly effective in roles such as sentry duty, message delivery, mine detection, and even rescuing wounded soldiers in battle zones.
Their alert presence and fearless demeanor served as a vital line of defense for U.S. troops, especially in the Pacific Theater during World War II.
History
The Doberman Pinscher traces its origins back to the 1890s in Apolda, Germany, where Karl Friedrich Louis Dobermann, a tax collector and dogcatcher, set out to create a loyal and protective companion. By crossing breeds like the Rottweiler, German Pinscher, Black and Tan Terrier, and Weimaraner, he developed the robust and agile Doberman we know today.
The breed was registered with the American Kennel Club in 1908, and its popularity grew among both civilian and military circles. Though modern military use has declined due to their sensitivity to extreme climates, Dobermans remain legendary for their wartime contributions and are still utilized in specific, controlled deployment missions.
Fact: The Doberman Pinscher was extensively used by the U.S. armed forces during World War II for scouting, message delivery, and guarding.
6. Rottweiler
Rottweilers are a commanding presence on the battlefield, known for their strength, stamina, and unwavering loyalty. These formidable dogs are more than just muscle; they possess a deep-rooted sense of duty and an ability to remain focused under pressure.
Their sheer power and powerful bite force make them ideal for security operations, especially in high-risk areas where deterrence and protection are key. They form strong bonds with handlers and perform best when given structured tasks in military and security environments.
History
The lineage of the Rottweiler traces back to ancient Rome, where they were bred from mastiff-type dogs to drive and guard livestock during military conquests.
As Roman legions moved into present-day Germany, these dogs became the ancestors of what we now know as the Rottweiler. Centuries later, they served in the cattle town of Rottweil, earning the name “Butcher’s Dog.”

During World War I and World War II, Rottweilers were employed by the U.S. military as messengers and guard dogs. Their versatile nature later saw them take on roles in police work, search and rescue missions, and even as early guide dogs for the blind.
Fact: These search and rescue dogs served as messenger and guard dogs in both World War I and World War II, proving their resilience and loyalty in critical missions.
7. Boxer
With their muscular frame, lively spirit, and unwavering loyalty, Boxers have served valiantly as U.S. military dogs. Their intelligence and composure under pressure once made them a top choice for communication roles, particularly during times when radio systems were unreliable.
Able to dash across battlefields while dodging chaos, Boxers were trained to deliver messages between handlers, making them a critical lifeline during World War operations.
History
The modern Boxer traces its lineage to late 19th-century Germany, where breeders refined it from the now-extinct Bullenbeisser, a powerful hunting dog once used to track large game like boar and bear. By selectively breeding with smaller mastiff-type dogs from England, the Boxer emerged as a sleeker, more agile companion suited for a range of working roles.
Its name comes from its unique tendency to “box” with its front paws during play or confrontation. Although the American Kennel Club first registered the Boxer in 1904, its popularity surged in the 1950s when a show-winning Boxer named Bang Away captivated American hearts.
Fact: During both World Wars, Boxers were employed as messenger dogs due to their calm demeanor and dependable strength under battlefield stress.
Conclusion
Military working dogs are more than just loyal companions; they are vital assets on the battlefield, serving with courage and precision. From the fearless German Shepherd to the versatile Boxer, these breeds exemplify intelligence, strength, and a keen sense of duty. Their ability to carry messages, detect threats, and support their human counterparts in high-stress environments highlights the indispensable roles they play in military operations. These dogs are trained rigorously by expert dog trainers to respond swiftly and remain composed in the face of danger, proving their worth time and again.
Equipped with a keen sense of smell, many of these dogs excel in explosive detection, search and rescue, and even therapeutic roles post-deployment. Their loyalty and adaptability make them unmatched partners in both combat and peacetime missions. While breeds like the German Shepherd and Belgian Malinois remain the cornerstones of military service, the history and legacy of other breeds, such as the Boxer, continue to underscore the evolving yet timeless bond between soldiers and their canine warriors.


