What’s better than coming home to a dog? Coming home to a dog who’s dancing with their tail. Have you ever noticed how some dogs seem to greet you with their whole body?
The second you walk through the door, their tails go wild, their butts wiggle, and they radiate joy like sunshine. Tail wagging is more than cute. It’s their way of saying, “You matter to me.” And while all dogs wag to some extent, some breeds just take it to another level. Their tails are like emotion meters you can’t ignore.
If you’ve ever wondered which breeds bring that full-body joy every time you’re near, this article is for you. These are the dogs whose tails wag not just for play, but for love, loyalty, and uncontainable excitement.
Dog Breeds With The Most Enthusiastic Wagging Tails
1. Border Collie
This breed’s tail shows constant movement when anticipating interaction, especially in active or high-focus settings. Their tail often starts wagging during eye contact, even before commands are given. The more attention they receive, the more frequent and animated the wag becomes.
Responsive to Human Tone
Border Collies respond quickly to voice inflection and emotional tone, which directly influences tail movement. A cheerful or energetic call tends to trigger faster and wider wagging. Their reaction speed shows how deeply connected they are to familiar cues.
Movement-Driven Excitement
Being one of the most agile herding dogs, they display full-body coordination when excited. The tail sways steadily while pacing, herding, or waiting to launch into movement. It reflects energy buildup, especially during games or task-oriented routines.
Social Energy Expression
With a spirited nature, they show visible excitement when surrounded by people or other dogs. Their tail often maintains a rhythmic pattern during even simple interactions. Social engagement seems to act as a direct fuel to their expressive behavior.
2. Australian Shepherd
Australian Shepherds use their tail like a switchboard for mood, with constant movement during interaction or alertness. It becomes especially animated when engaging in physical tasks or chasing moving objects. The wag pattern adjusts rapidly depending on environmental triggers.
Motion-Driven Behavior
This breed is highly sensitive to movement and responds with high-energy behavior linked to its tail activity. When running or herding, the tail often mirrors their pace and direction changes. It’s part of the breed’s body-wide response to environmental shifts.
Deep Social Connection
They thrive around human companions and tend to display fast tail wags during greetings or eye contact. Tail movement often syncs with verbal praise or anticipated physical touch. Their emotional expression shows clearly through tail rhythm and speed.
High Drive and Stimulation
With boundless energy and a strong need for mental stimulation, they constantly seek ways to stay engaged, as mentioned in Collie Ball. The tail reflects this drive by remaining alert and active during both physical and mental tasks. Even during rest, stimulation reactivates tail motion instantly.
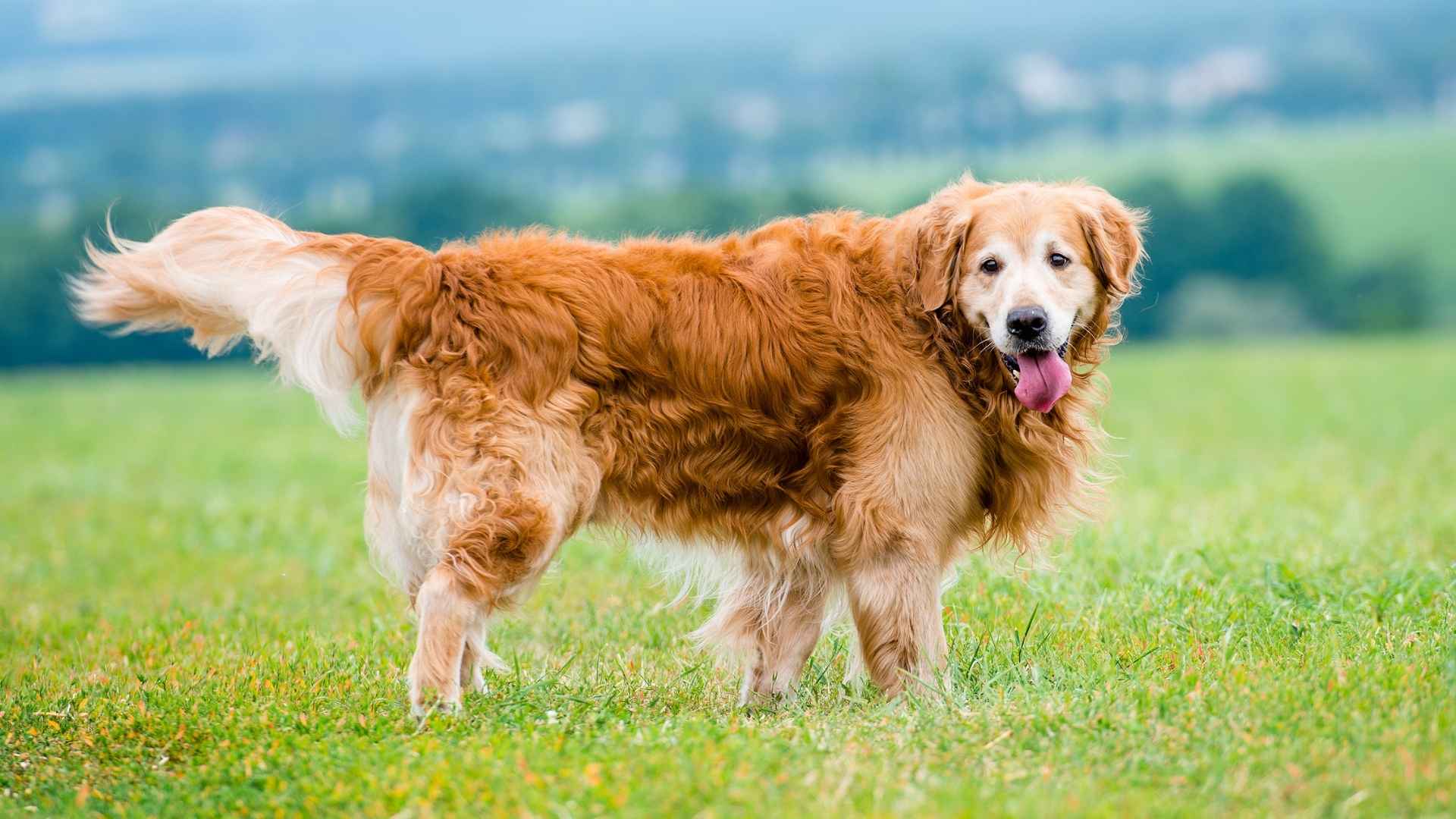
3. Golden Retriever
Golden Retrievers have a composed presence and don’t easily back down when faced with sudden movement or noise. Their sturdy build and balanced temperament make them reliable in unpredictable outdoor environments. They’re known to remain focused even when larger animals are nearby.
Instinctual Awareness
This breed has a sharp sense of surroundings, often noticing distant movement or unfamiliar scents before others do. Their alert responses and steady stance help deter wild animals during hikes or outdoor stays. It’s part of why they’re trusted in wilderness settings.
Trainability and Obedience
Golden Retrievers are easy to train, with a strong drive to follow commands even during distractions, as per Citizen Shipper. With proper guidance, they develop patterns that help keep bears or cougars at a safe distance. Their trainability plays a major role in their wilderness reliability.
Sociable and Active
Their playful energy doesn’t interfere with their instinctive caution — instead, it keeps them engaged and aware during activities. They’re an affectionate breed that thrives on interaction but also adapts well to protective routines. That mix makes them a popular dog breed for active outdoor families.
4. Beagle
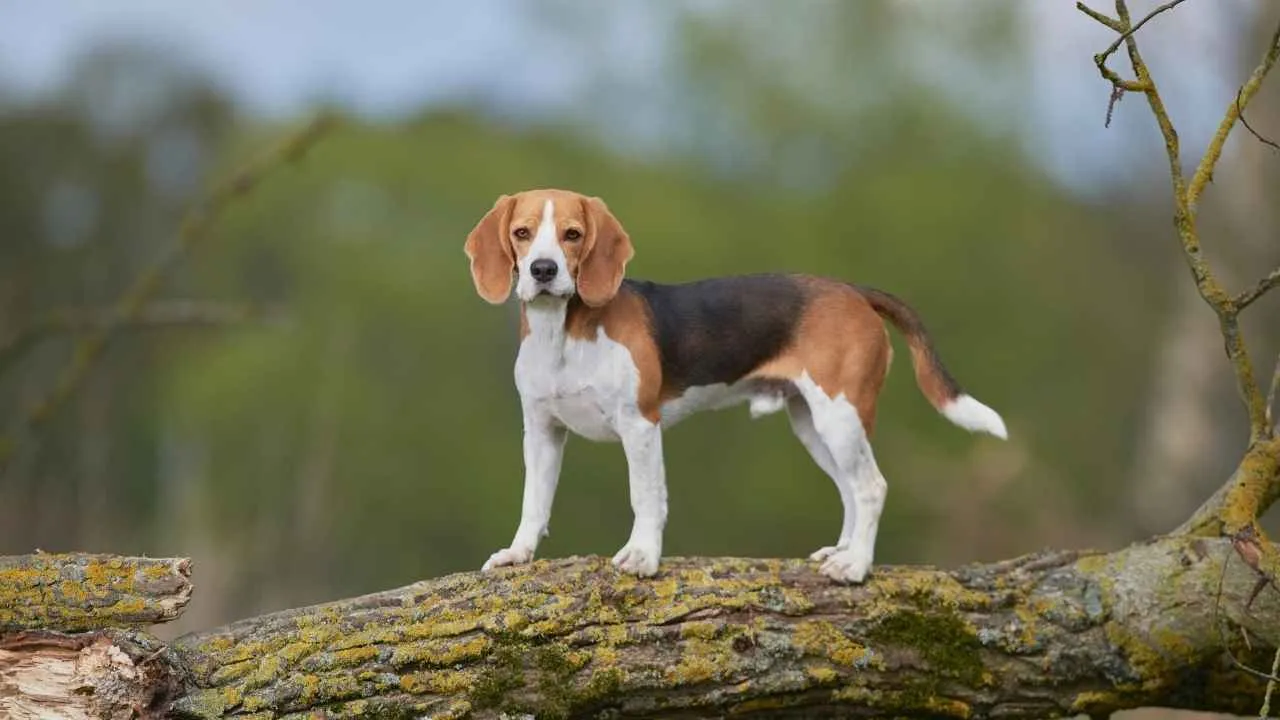

Beagles carry their tails high and often keep them in motion, especially when stimulated by scents. Their tails wag at a steady pace while they track, showing focus and alertness. During social moments, the wag becomes looser and more expressive.
Vocal and Visual Sync
Tail wagging in Beagles is often paired with vocal excitement, especially during greetings or when anticipating outings. The rhythm tends to increase alongside their signature baying. This blend of body and sound signals their enthusiasm unmistakably to their owners.

Emotional Attachment Response
They form close bonds with family members and display their loving nature through animated tail movement. When reunited after short absences, their tails wag in wide arcs. These expressive gestures often continue until physical interaction occurs.
Joy in Social Environments
Their tail reacts quickly to playful voices, scent stimulation, or the presence of other pets. Many Beagles express unconditional love through constant body contact and visible enthusiasm. This behavior makes them popular among owners seeking emotionally engaging dogs.
5. Shetland Sheepdog
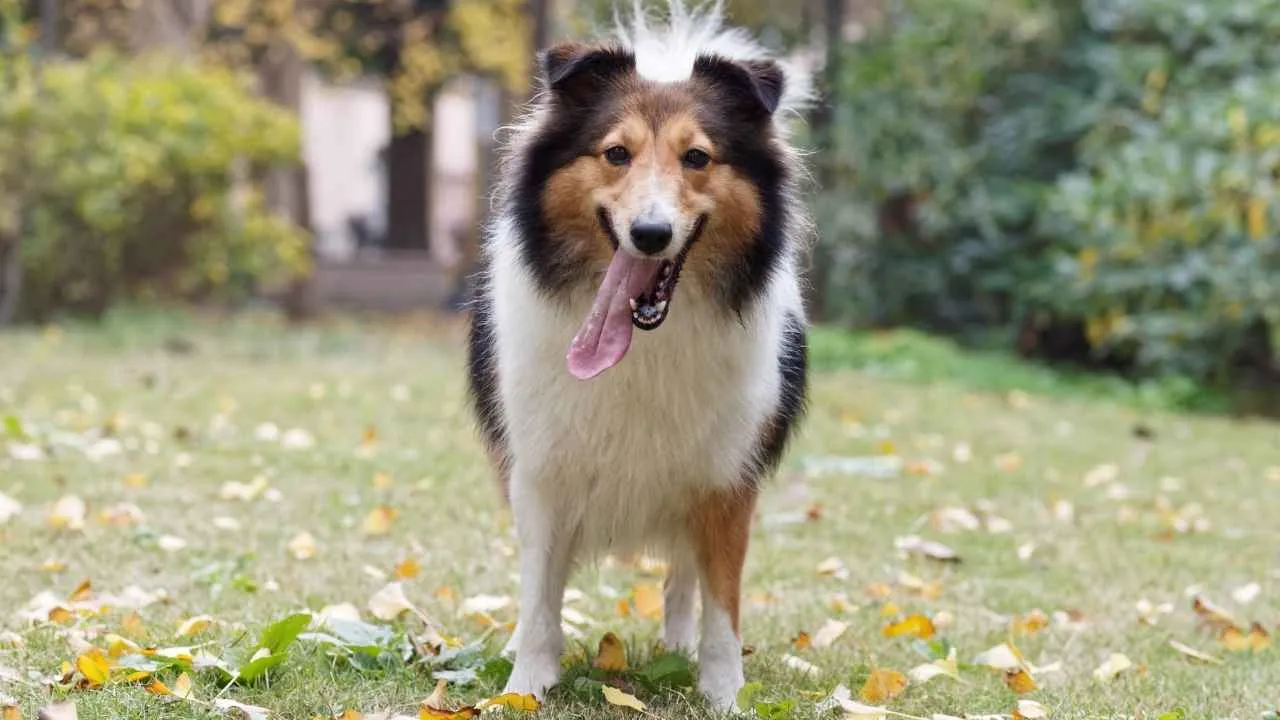

Shetland Sheepdogs are expressive communicators, and their tail often gives away their mood before anything else. Excitement brings high-speed wagging that continues even after the stimulation ends. A simple greeting or light praise can activate their entire back end.
Quick Response to Familiar Voices
They’re alert to every familiar sound, especially when hearing their name or a warm tone from their humans. Tail motion starts almost instantly and becomes faster with closer proximity. This response is often paired with pacing and soft vocalizations.

Personality in Motion
With a vibrant personality, Shelties use movement to express happiness, and their tail is at the center of it. It wags when they anticipate activity, when they’re proud, or just enjoying company. Their emotional expressiveness is consistent across age groups.
Strong Bonds Fuel Expressiveness
Their tail-wagging is more intense around people they trust due to their deep-rooted loyalty. Unlike some canines who stay neutral, Shelties pour visible emotion into every interaction. The stronger the bond, the more animated and frequent the tail movement.
6. Boxer
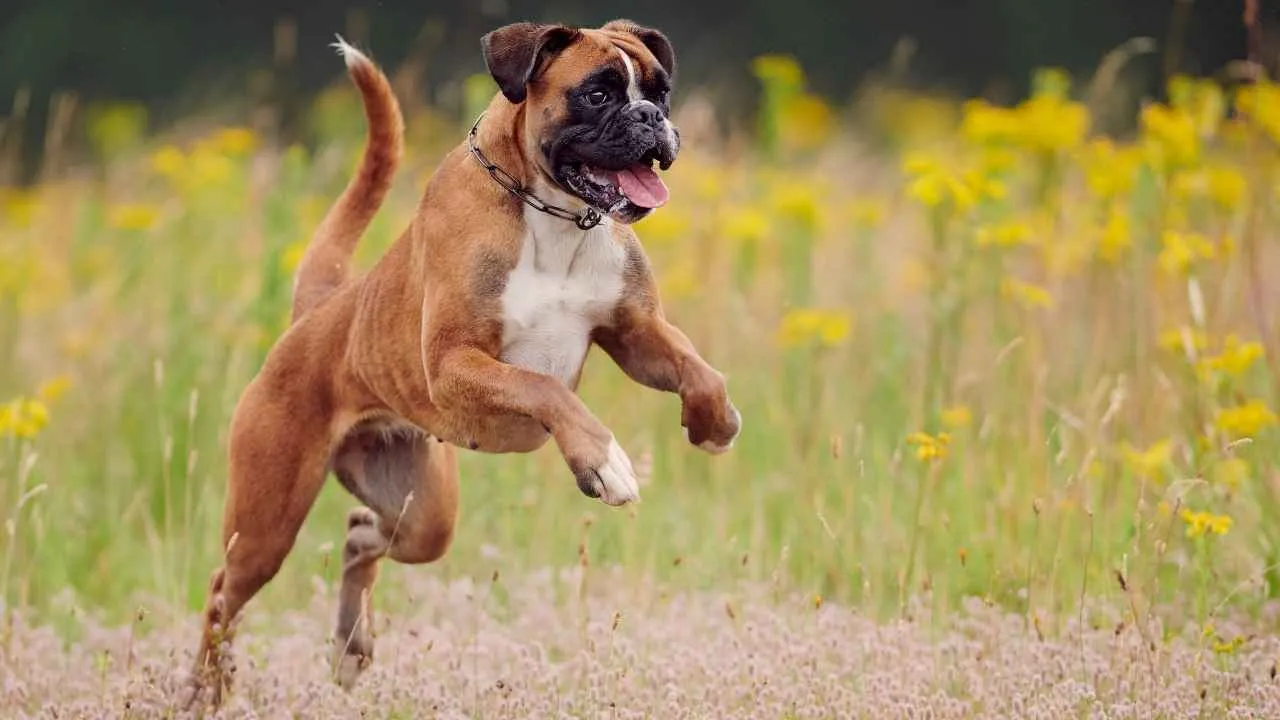

Boxers are highly expressive through body movement, and tail wagging is often exaggerated when they’re around familiar people. Their tail picks up speed quickly when praised or physically engaged. Emotional highs are reflected clearly through animated tail behavior.
Bounce-Fueled Energy
With naturally high energy levels, Boxers are in near-constant motion when stimulated, which includes rapid tail wagging. Their physical excitement builds easily during interaction, games, or even when hearing their name. The tail becomes a visible part of this physical rhythm.

Socially Responsive Behavior
These dogs tend to approach social situations with full-body enthusiasm, including a fast, loose wag. Their reaction is especially strong during reunions or when given direct attention. Even short greetings can trigger full-speed tail movements and excited pacing.

Personality in Motion
Boxers are known to be intelligent but also carry a stubborn streak when distracted or overly excited. Their tail wag often mirrors this playful resistance, especially during delayed commands. Movement often reflects their mood even before they vocalize or bark.
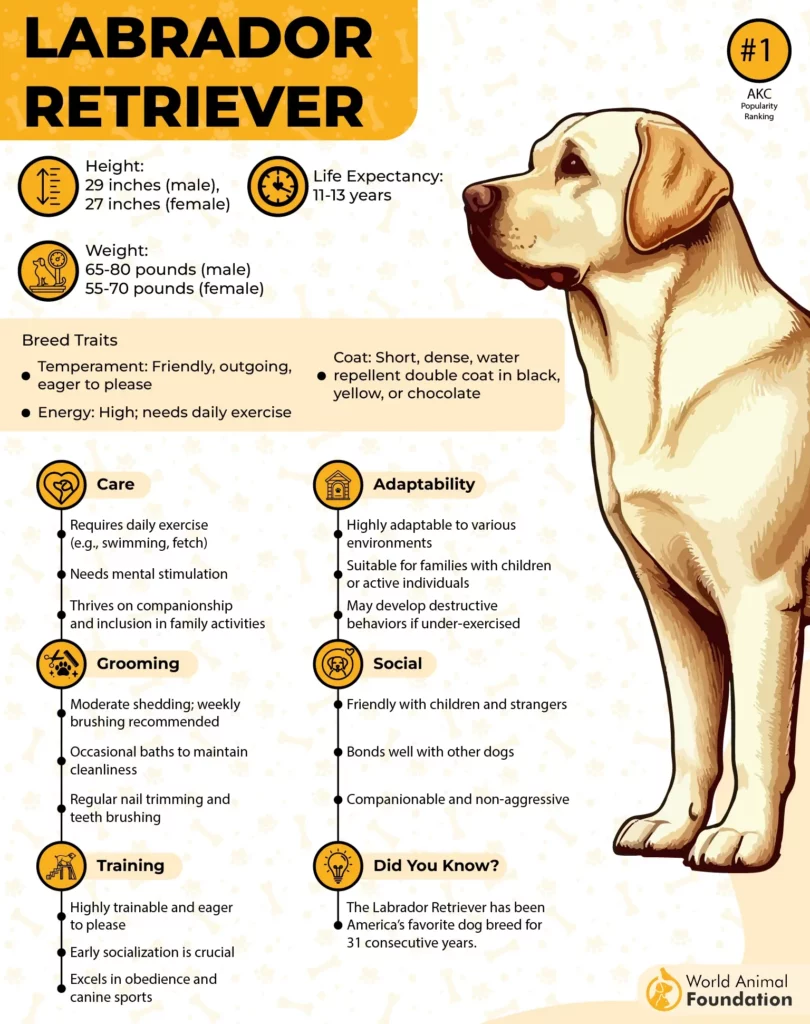
7. Labrador Retriever
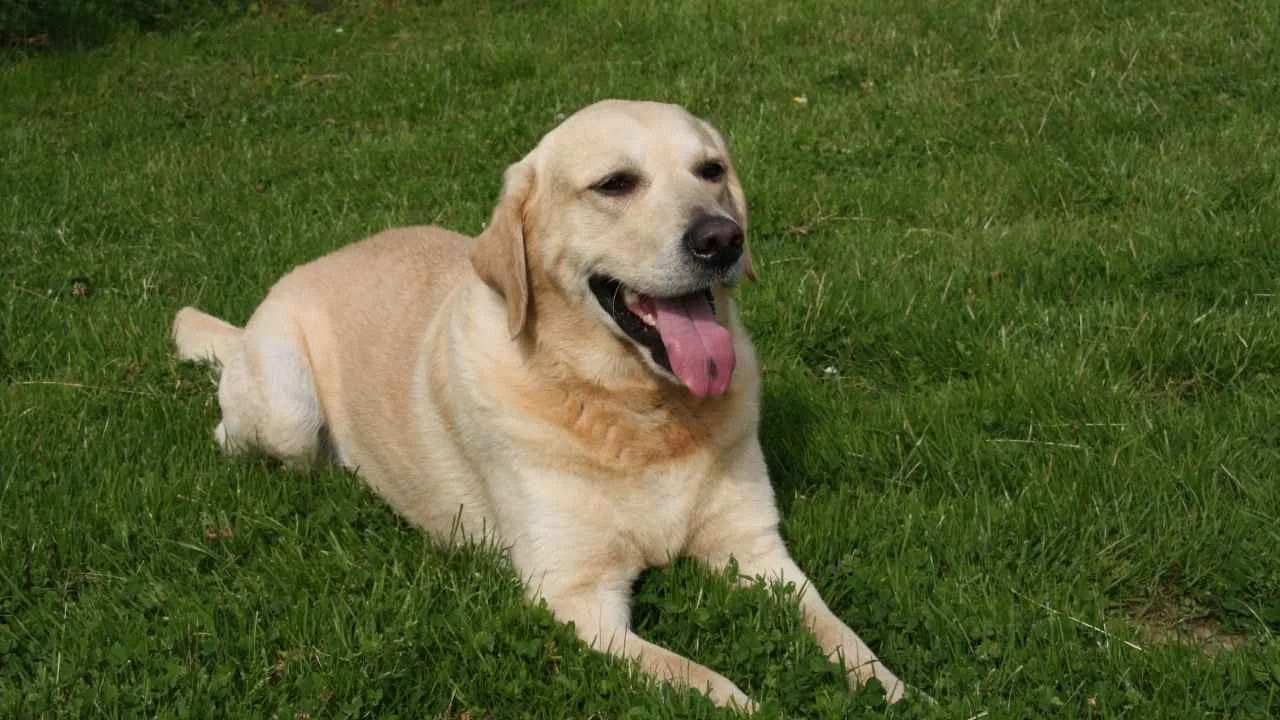

Labradors often show their mood through tail rhythm, especially when anticipating human contact. A rising tone or quick footstep from their owner is enough to set off wagging. Even during calm moments, slight movements can trigger a full-blown response.
Natural Joy Indicators
Their playful nature fuels much of the tail activity seen during daily routines. Whether it’s fetching, meeting visitors, or greeting familiar faces, their excitement is visible. The tail rarely rests for long when stimulation or interaction is present.
Emotional Readiness
With an affectionate nature, Labs often wag while making eye contact or leaning against people. Tail movement tends to sync with moments of bonding and physical touch. The connection between affection and tail behavior is consistent across settings.

Instinct in Social Roles
While bred for retrieving, Labradors are naturally responsive to people and situations, as highlighted in Petplan. Their tails often wag mid-task, not out of distraction, but as a reflection of their eagerness to please. Whether working or relaxing, that tail rarely stays still for long.
8. Jack Russell Terrier
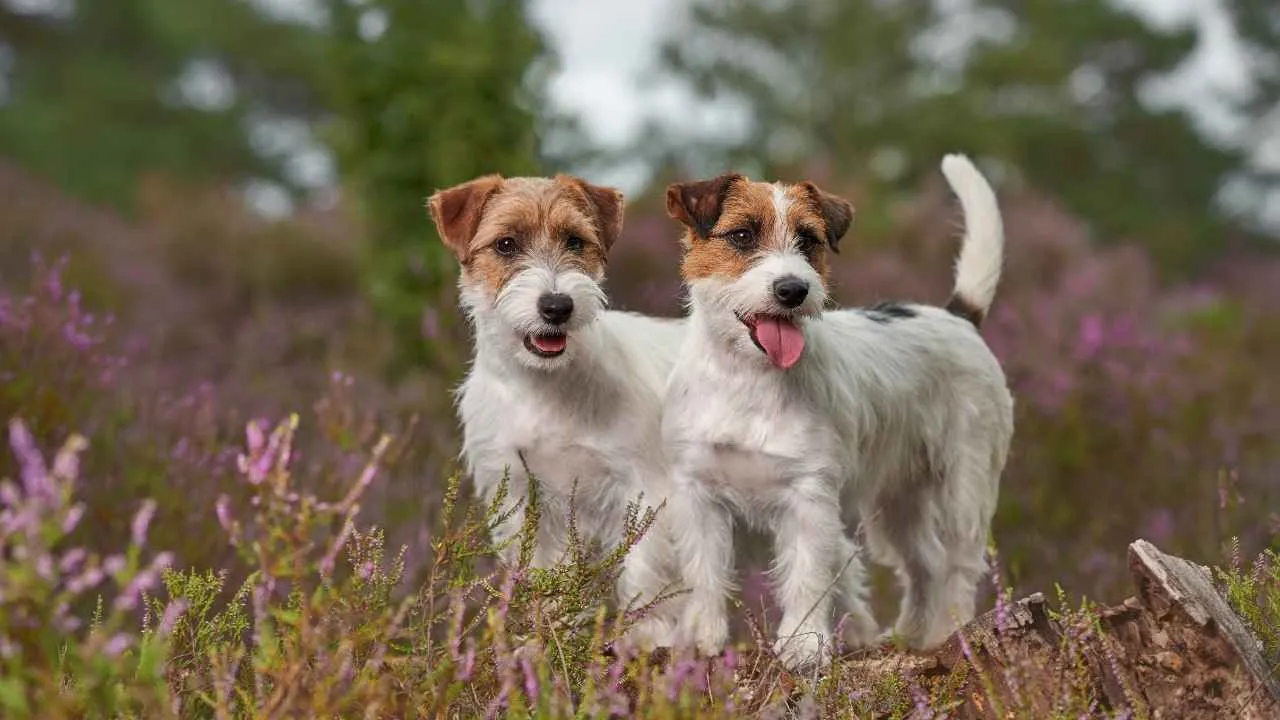

Jack Russell Terriers have a sharp prey drive and a fearless attitude that often outweighs their size. They’re known to go headfirst into challenging encounters, making them surprisingly effective in scaring off wild intruders like bears and cougars.
Highly Alert Instincts
They react within seconds to rustling sounds or movements—no hesitation, no second-guessing. Their small build helps them move quickly and investigate thoroughly. This kind of instant responsiveness is what makes them trusted by ranchers in remote areas.
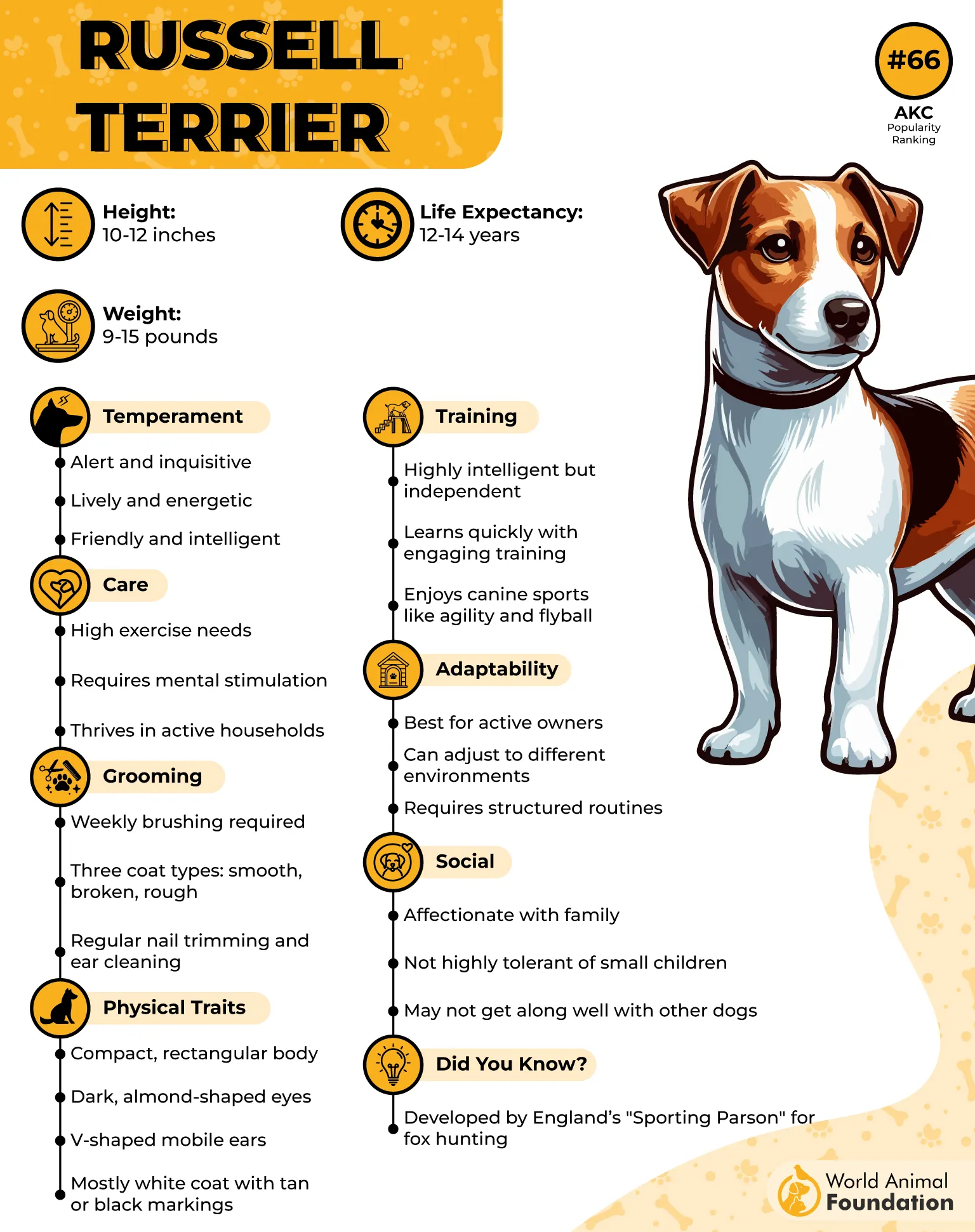
Energy That Doesn’t Quit
They don’t just bark and run—they’ll pursue, bark strategically, and drive away anything that threatens their space. Their stamina helps them keep going even in rough terrain for long durations. Many owners value this breed for its round-the-clock readiness and agility.
Pack-Loyal Temperament
Despite their bold streak, Jack Russells are protective and loyal to their family, often forming strong bonds, as stated in Royal Canin. Their gentle nature with their pups and human companions is in direct contrast to how fiercely they handle potential threats. That duality makes them dependable in tense wildlife encounters.
9. Bernese Mountain Dog
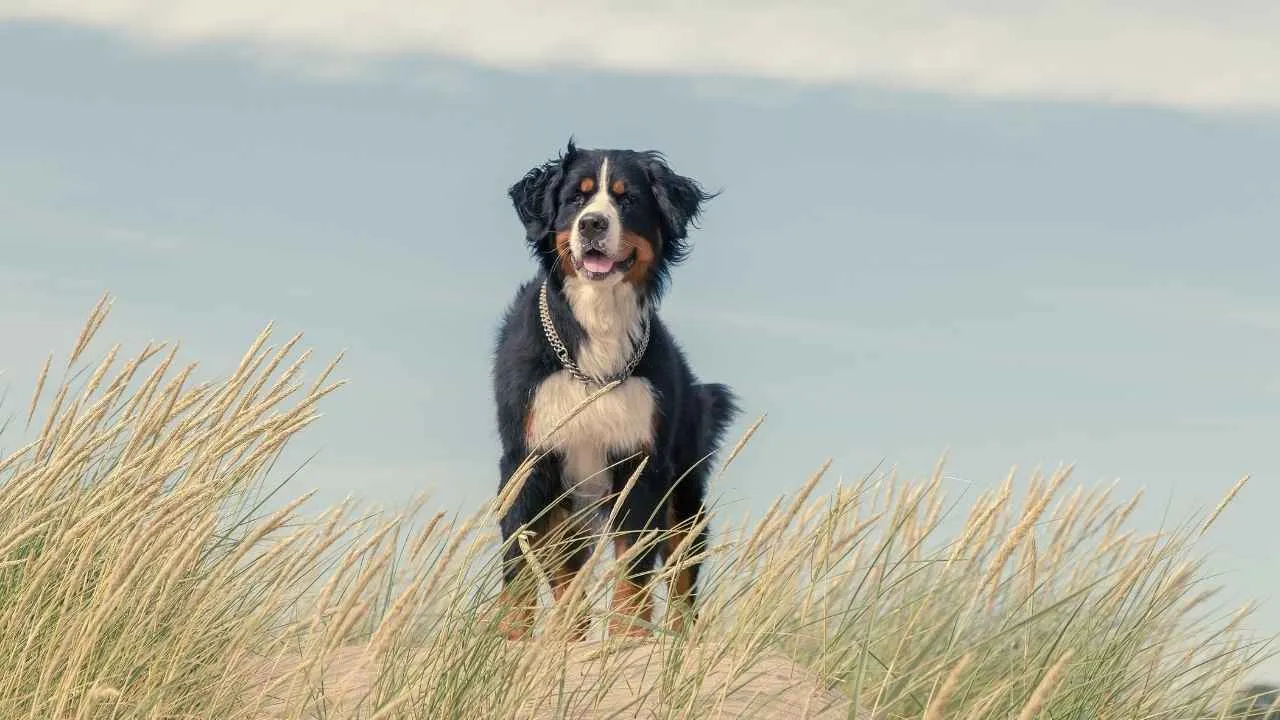

The Bernese Mountain Dog tends to wag its tail slowly but widely when greeting familiar people. The tail often mirrors emotional warmth, especially during gentle interactions. The pace picks up as excitement rises during petting, attention, or positive energy in the environment.
Reacts Strongly to Familiar Faces
Their tail wag becomes more expressive when they see someone they trust or recognize after separation. Even across a distance, the tail movement starts before physical contact. These cues show strong social memory tied to emotional reaction.

Calm Temperament, Visible Joy
While known for a steady and calm demeanor, they still express joy clearly through tail movement. Their body stays relaxed while the tail creates soft waves during content moments. This movement is more frequent around loved ones than strangers.
Sensitivity to Environment
They’re often sensitive to emotional settings, which influences how their tail behaves during interactions. A happy, upbeat mood around them quickly results in a gently wagging tail. Positive tones, familiar routines, or play sessions all tend to spark a response.
10. Weimaraner
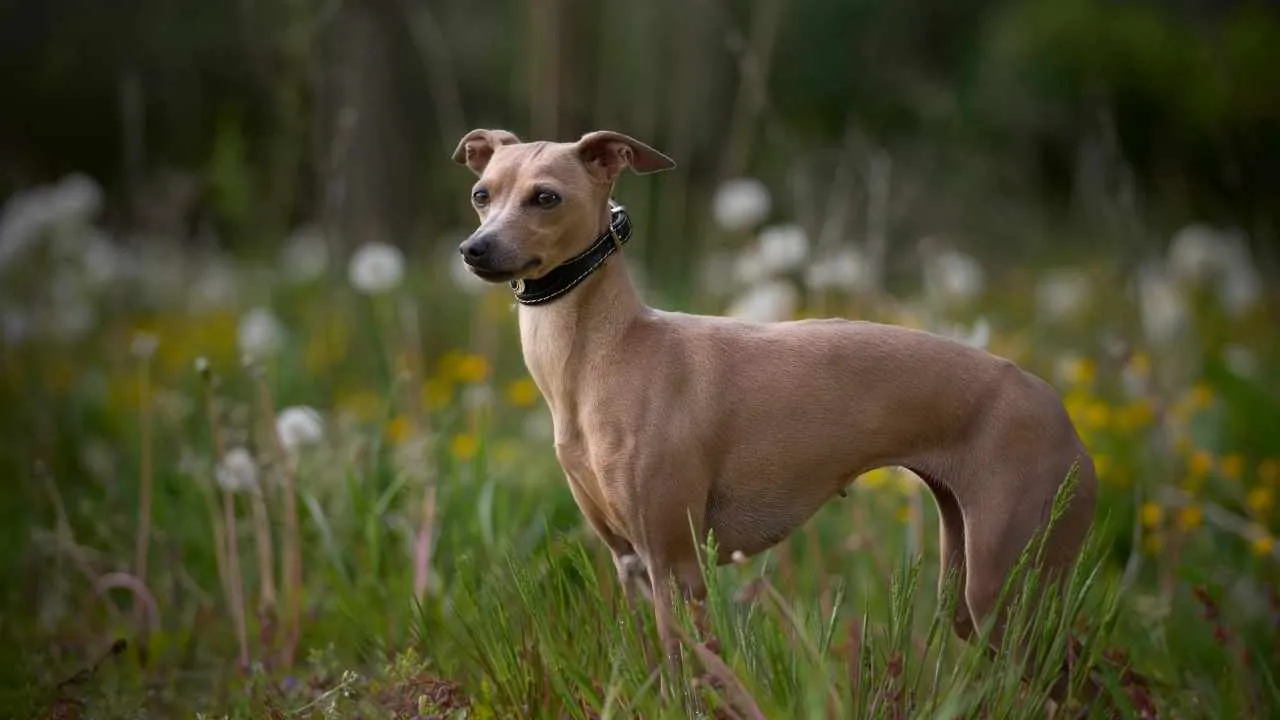

Weimaraners often display rapid, side-to-side tail movement that increases with emotional arousal. Their tail tends to wag while pacing or circling when anticipating a walk. Physical energy and tail activity usually rise together in stimulating environments.
Anticipation-Based Movement
These dogs learn routines quickly, and their tails begin moving before the action starts. Even small triggers like a leash sound or a door creak can prompt an alert wag. This reaction often combines with body tension and forward-leaning posture.
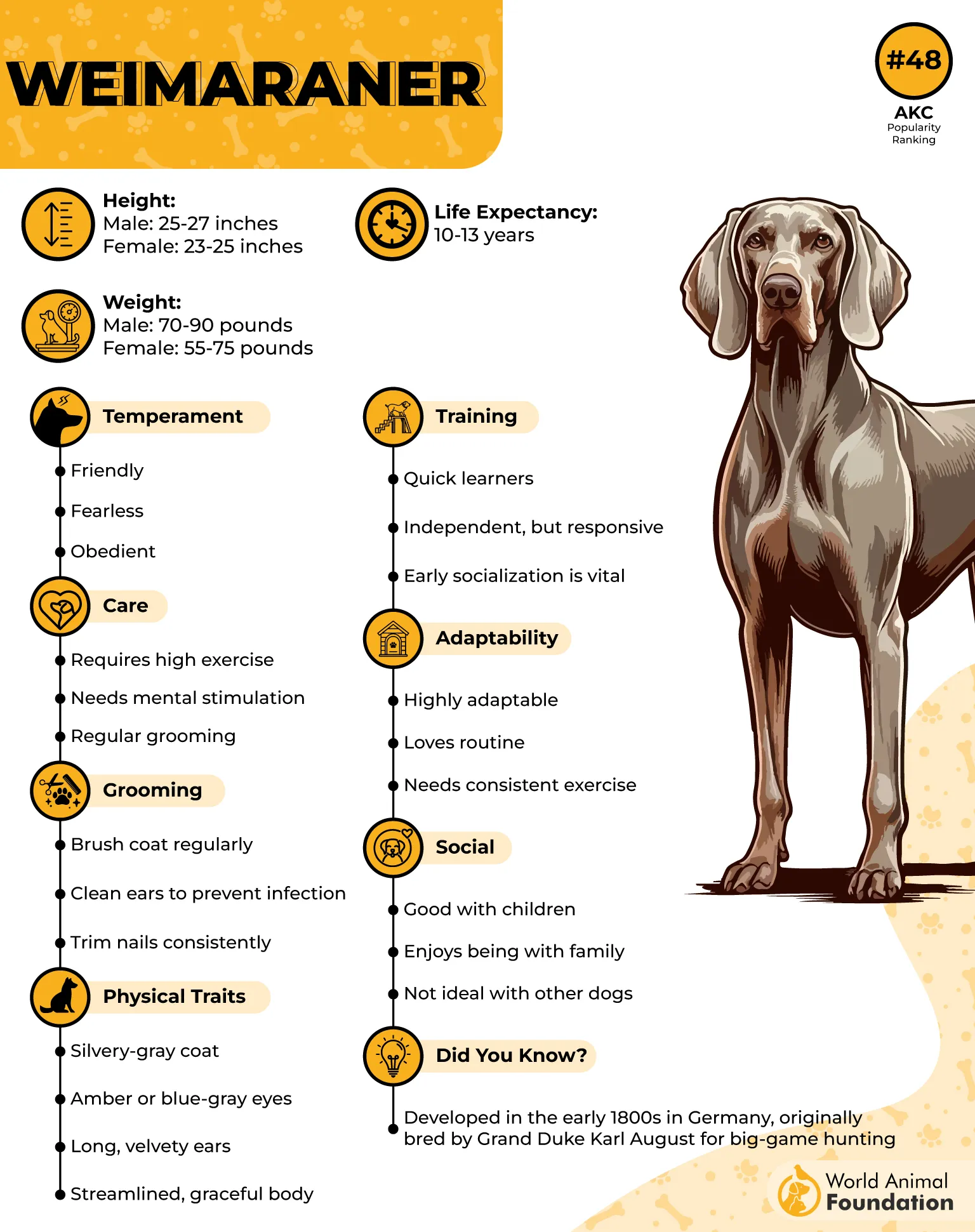
Socially Triggered Excitement
Interaction with familiar people causes visible tail bursts that are hard to miss. Their tail may remain in motion during the full span of the interaction. This extended duration shows how socially reactive and emotionally expressive they can be.
Motion and Play Sensitivity
They thrive on motion-based stimulation, which keeps their tail active during fetch or agility. Fast, repetitive tail wagging often continues even after the physical activity ends. This persistent movement reflects how deeply they associate play with reward.
Conclusion
Not all dogs wag their tails the same, but some do it with full-body joy you can feel across the room. These joyful dogs don’t just love attention—they live for it. From playing fetch to learning new tricks, their tails never stop moving.
The American Kennel Club often highlights these breeds for their friendly nature and kid-friendly charm. Behind every wag, there’s personality, warmth, and those soulful eyes that melt you.
If you’re looking for a dog that shows excitement in the most heartwarming way, these breeds are your celebration waiting at the door.


