Not all dog breeds are equally healthy. Some have been bred in ways that make them far more vulnerable to disease and discomfort.
While dogs bring incredible joy to our lives, choosing a breed without considering health risks can lead to years of veterinary visits and painful experiences. Problems such as joint disorders, respiratory trouble, and heart disease are unfortunately built into the genetics of certain popular dogs.
This is not about avoiding dogs, but about being realistic when selecting a companion who can live a full and happy life. Awareness of these risks is the first step toward responsible ownership.
To help future owners make better decisions, this article will outline the breeds known to face the most significant health challenges.
Best Dog Breeds to Avoid Due to Health Issues
1. English Bulldog
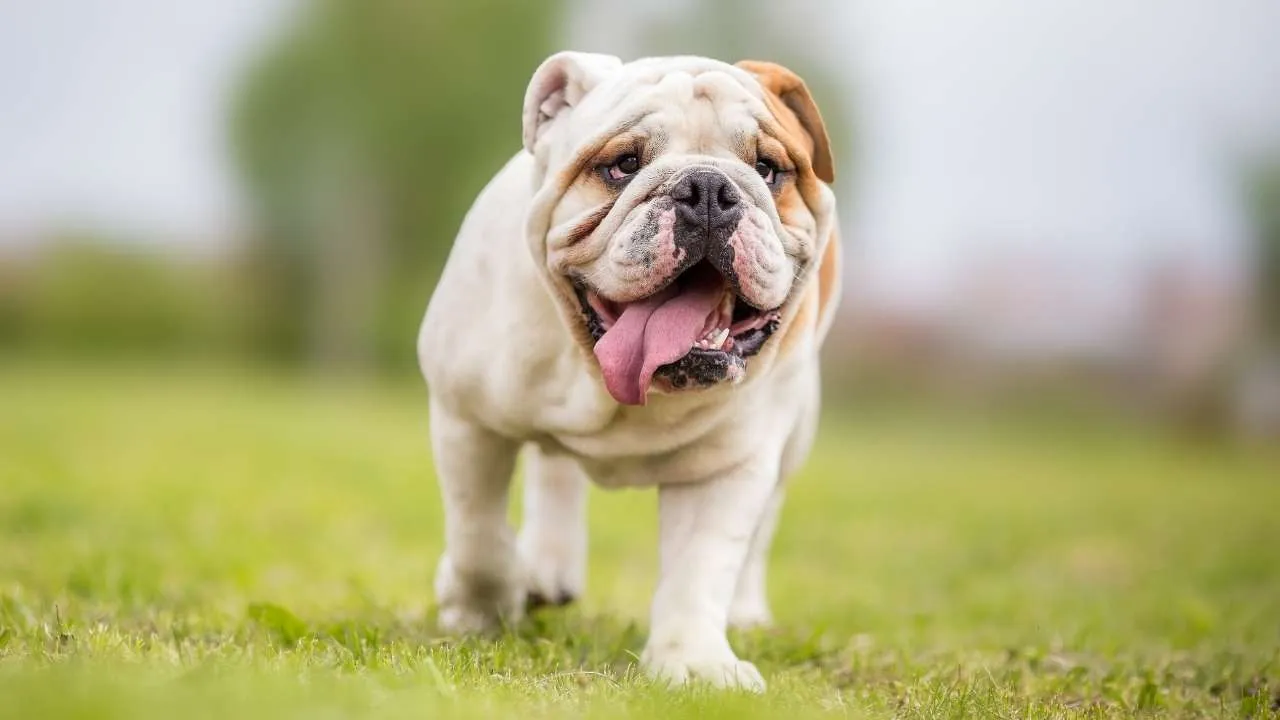

The English Bulldog was shaped by selective breeding that emphasized compact bodies and flat faces. These physical traits, while distinctive, have created long-term vulnerabilities. Many of the breed’s most recognizable features are linked directly to chronic health concerns.
Common Structural Problems
Hip dysplasia is frequently diagnosed in this breed, leading to painful mobility issues as the dog ages. Their broad chest and shortened legs place uneven stress on joints. This skeletal imbalance often contributes to difficulty with walking and running.
Breathing and Weight Challenges
Brachycephalic Obstructive Airway Syndrome is common in bulldogs, making it hard for them to tolerate heat or vigorous activity, as PetMD highlighted. Owners must carefully monitor diet and exercise to help them stay at a healthy weight. Without proper management, breathing and stamina issues worsen.
Additional Medical Risks
Other recurring conditions include luxating patella, skin fold infections, and obesity when exercise is limited. Vets often recommend early screening for joints and weight management routines. Preventive care is essential to prolong comfort and mobility.
2. German Shepherd
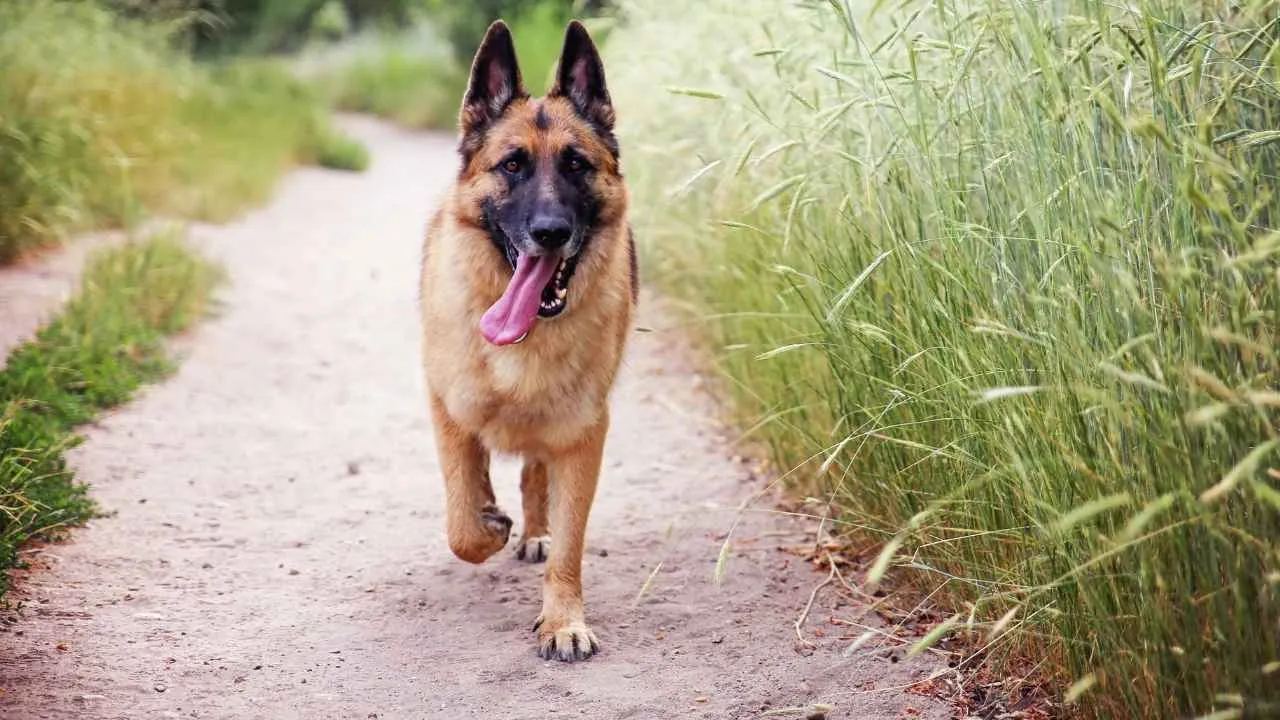

German Shepherds have a long history of service as guard dogs, military partners, and loyal family protectors. Their intelligence and drive for activity make them versatile, but the same physical traits that give them power and agility also leave them vulnerable to certain health problems.
Common Medical Concerns
These dogs are prone to musculoskeletal conditions that affect mobility and long-term comfort.
Hip dysplasia and elbow dysplasia remain leading issues.
Bloat, allergies, and even heart conditions can also appear in the breed.
Preventive care and early screenings are key to keeping a dog healthy.

Care and Prevention
Managing weight, encouraging controlled exercise, and sticking to a balanced diet all reduce strain on their joints. Proper meal planning also lowers the risk of bloat, a condition that requires emergency treatment. Simple lifestyle adjustments play a major role in extending their active years.
Considerations for Families
Pet parents need to understand that while German Shepherds are excellent companions, their long-term needs are demanding. Regular vet checkups, joint support supplements, and responsible breeding practices can significantly lower risks.
3. Great Dane
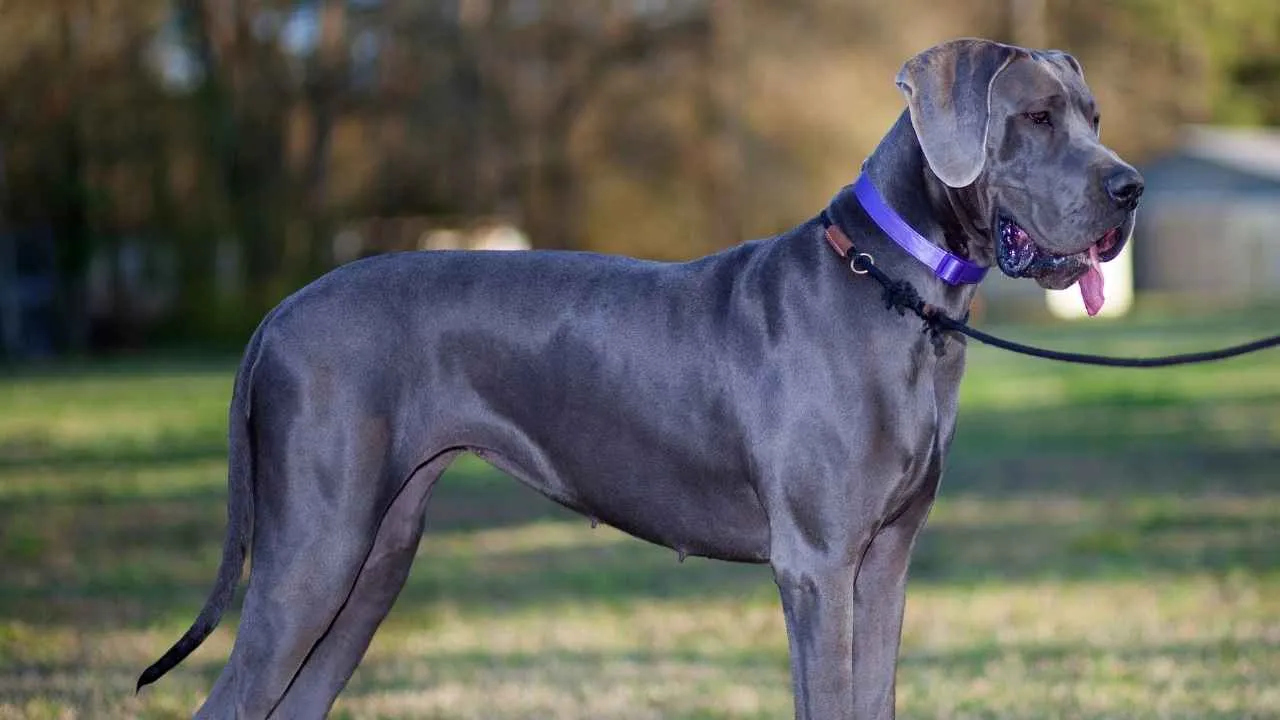

Great Danes stand among the tallest of all breeds, often reaching heights that surpass most family dogs, as mentioned in the AKC. Their large frame and calm personality have earned them the title of gentle giants. While their appearance is striking, such size also contributes to their predisposition to serious health conditions.
Predisposed Health Problems
They face a higher risk of orthopedic and cardiac problems compared to generally healthy dogs of smaller stature. Common concerns include hip dysplasia, dilated cardiomyopathy, and osteosarcoma. These conditions require careful monitoring and consistent veterinary care to be managed effectively.
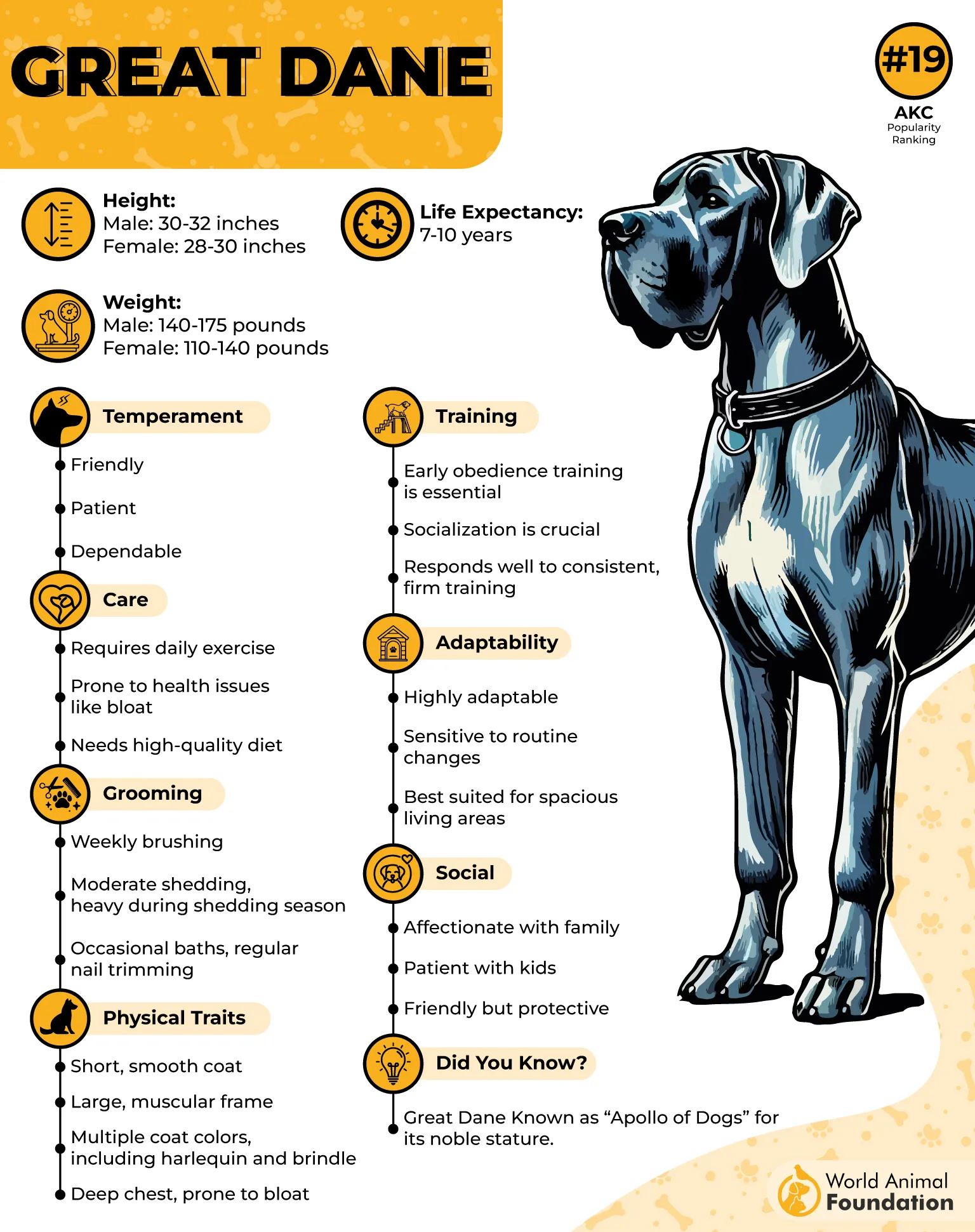
Bloat and Preventive Care
One of the most life-threatening issues in Great Danes is gastric torsion, commonly referred to as bloat. Steps that can help reduce this risk include:
Feeding several smaller meals each day
Avoid vigorous activity before and after eating
Using raised feeding bowls to limit excess air intake
Lifespan and Family Considerations
Their average lifespan is shorter than many dog breeds, with most living around 7 to 10 years. To keep your dog healthy, weight management, joint-supportive exercise, and early detection of disease are essential. Families should be prepared for both the rewards and the challenges of caring for such a giant breed.
4. Cocker Spaniel
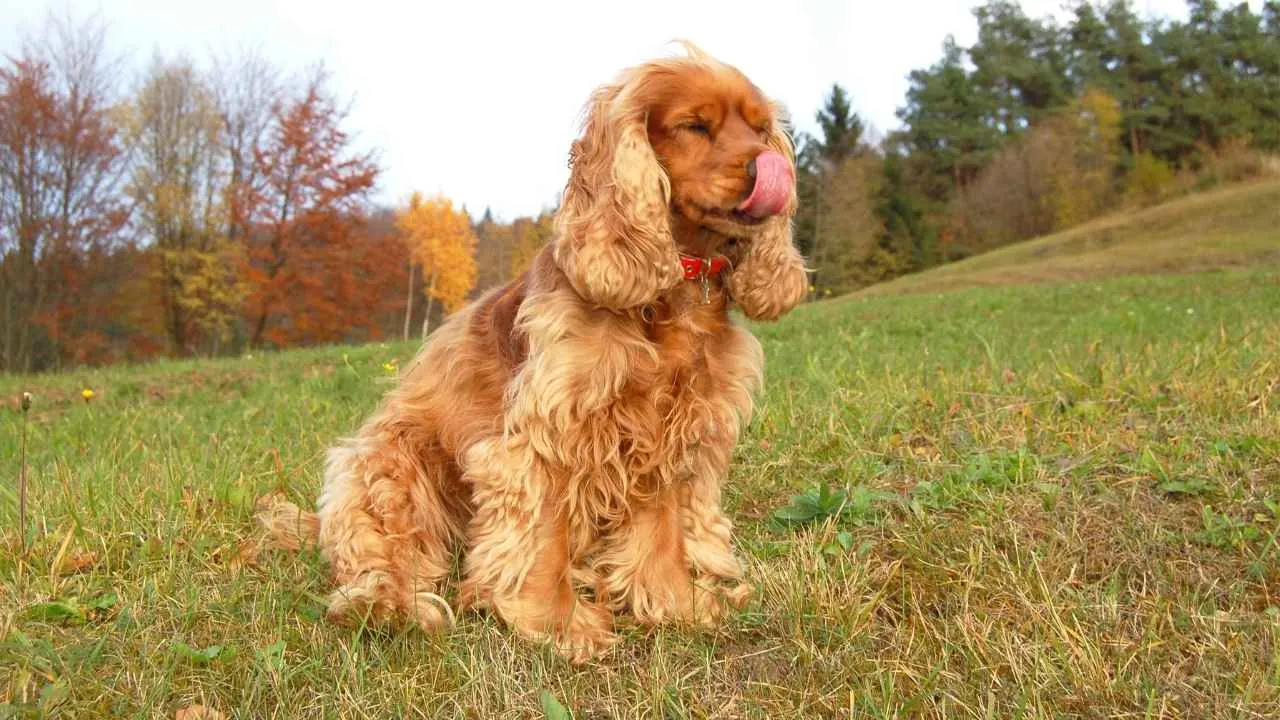

Cocker Spaniels are affectionate companions, well-loved for their gentle temperament and cheerful personality. Their size and adaptability make them suitable for both apartments and larger homes. This popularity, however, often overshadows the health challenges the breed can face.
Common Health Concerns
These dogs are prone to conditions that need consistent monitoring.
Ear infections are frequent due to their long, floppy ears.
Eye problems such as cataracts, glaucoma, and PRA often develop with age.
Heart conditions like mitral valve disease may appear later in life.

Mobility and Joint Issues
Hip dysplasia is a significant concern in this breed and can reduce comfort in daily activities. Managing weight and exercise routines helps ease pressure on joints. Families that emphasize a healthy lifestyle often see their dogs remain active longer.
Skin and Coat Maintenance
Regular grooming is essential, as skin allergies and seborrhea are common in Cocker Spaniels. Dryness, itching, and dandruff can become chronic if not addressed. Careful grooming habits and vet guidance are key to maintaining a healthy life for this breed.
5. Doberman Pinscher
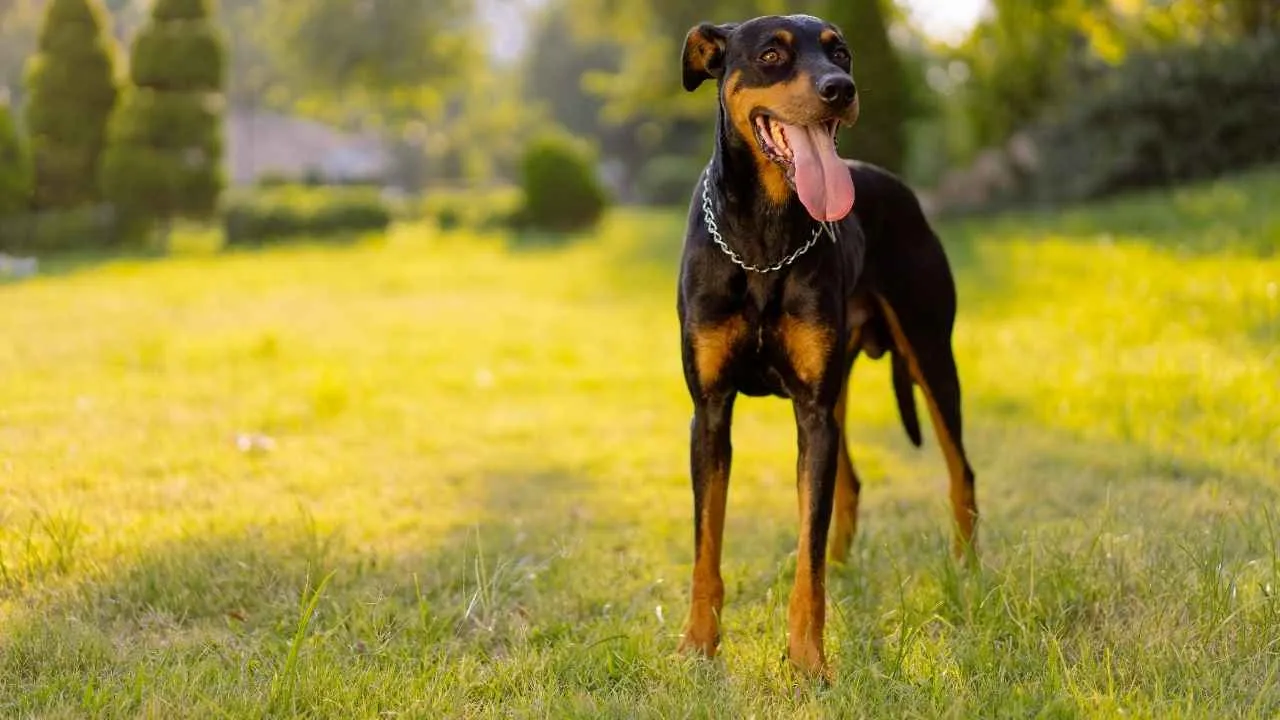

Dobermans are admired for their sleek build and working ability, but their health profile tells another story. Their active lifestyle often masks internal issues that can progress silently until they become severe. Families considering them should weigh both energy and risk.
Widespread Health Problems
This breed is prone to a list of medical conditions that often affect large dogs.
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is linked to sudden cardiac failure
Hip dysplasia and arthritis in later years
Blood clotting problems, such as coagulopathy
Such recurring problems make longevity a major concern.

Early-Onset Disorders
Another German-raised dog, the Dobermann, is a working breed that was built for protection, as Britannica claimed. However, kidney-related illnesses like glomerulonephropathy can develop at a young age and cause irreversible damage. These complications reduce quality of life despite strong genetics for performance.
Long-Term Care Demands
Managing a Doberman’s health often requires regular screening, dietary oversight, and advanced veterinary care. Conditions like coagulopathy or DCM can escalate quickly without careful management. For families, the responsibility extends beyond training into ongoing medical planning.
6. Pug
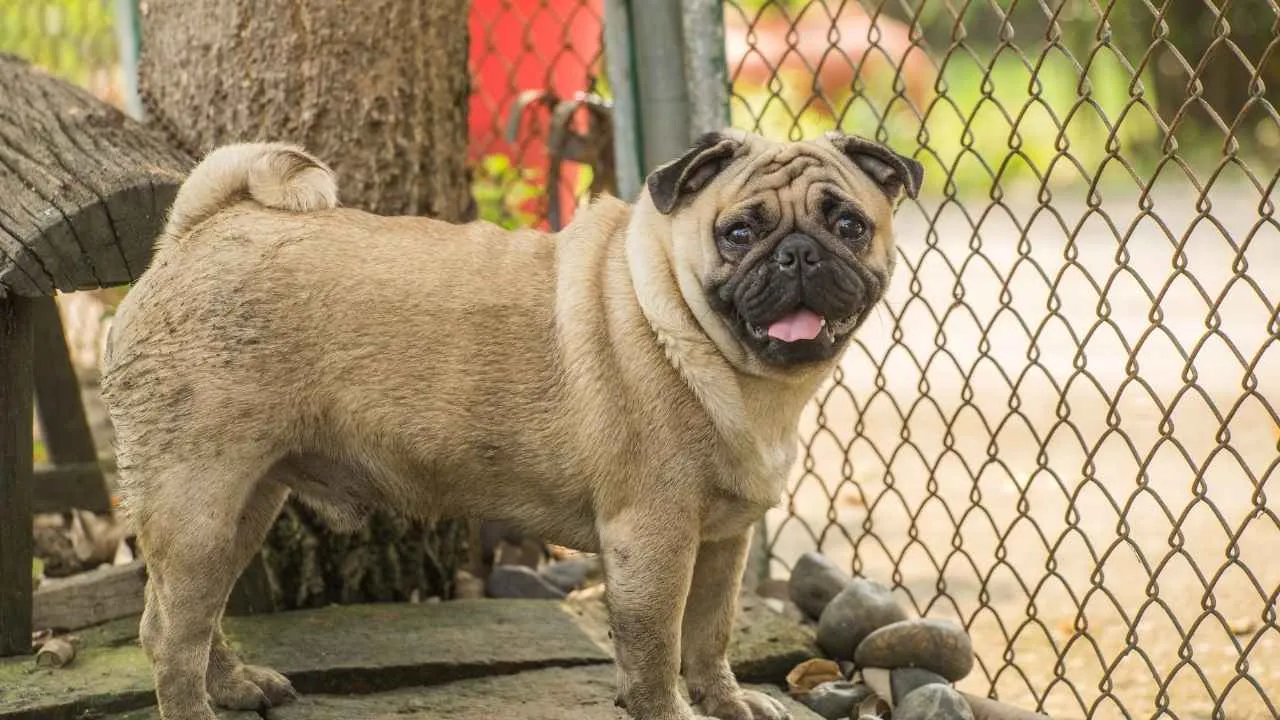

Pugs are among the most popular breeds admired for their compact build, wrinkled face, and curly tail. Their affectionate temperament makes them well-suited for families, and they often adapt easily to homes with children and other pets.
Breathing Difficulties
The short muzzle puts them at high risk of brachycephalic airway syndrome, a condition that makes breathing labored, especially during warm or humid days. Studies show they are over fifty times more likely to develop this than most other dogs. Careful management of activity and climate is essential to protect their comfort and safety.
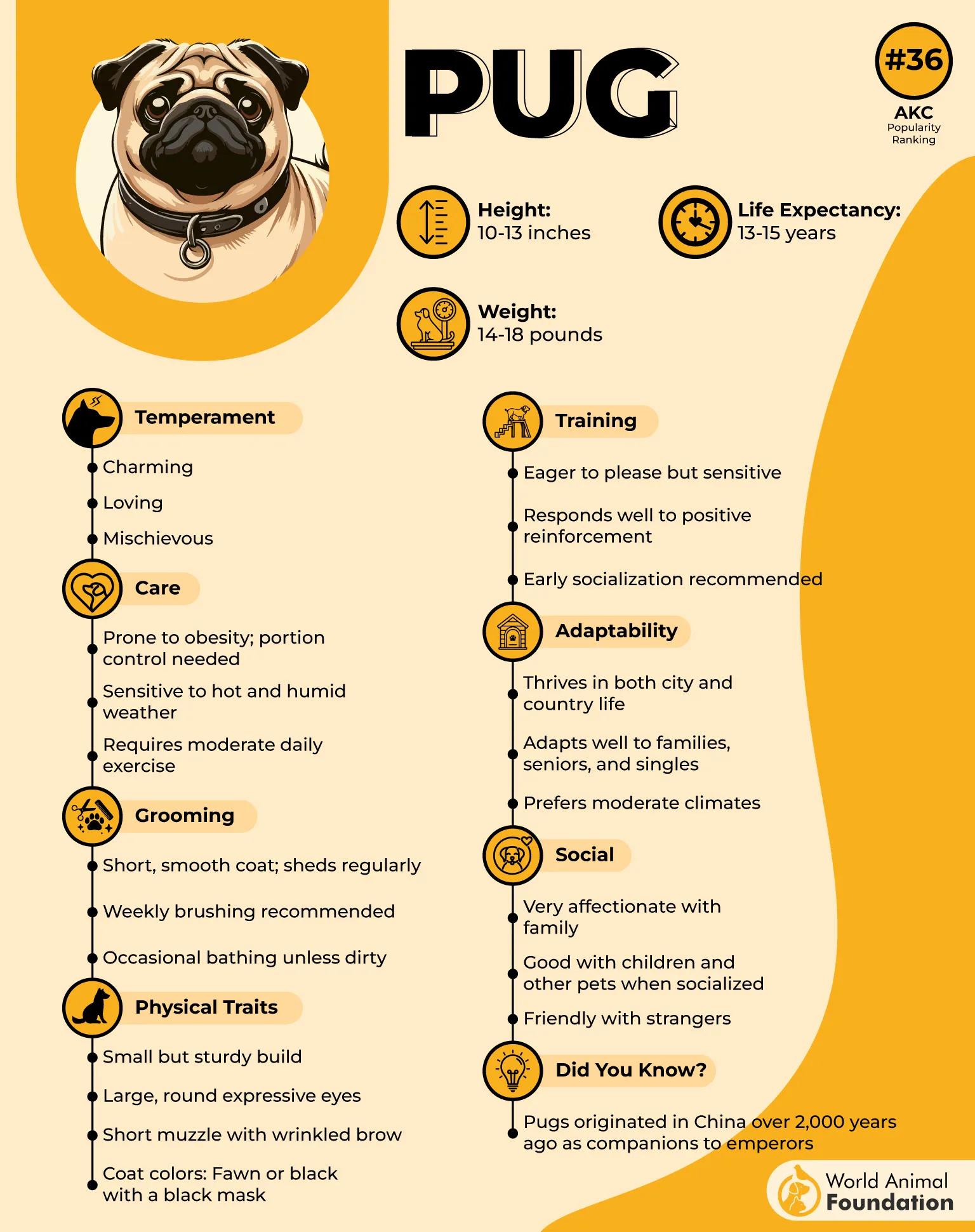
Common Medical Concerns
Their bulging eyes and shallow sockets leave them prone to painful conditions like corneal ulcers, progressive retinal atrophy, and chronic dry eye. Weight is another issue since they love food and tend to gain weight quickly, which in turn worsens respiratory and joint strain.
Hip dysplasia leading to arthritis and pain
Skin irritation from moisture trapped in facial folds
A tendency toward obesity without regular activity
Care Requirements
Owners must commit to vigilant upkeep to reduce risks. Routine cleaning of skin folds prevents infections, while portion control and steady exercise help with weight balance. Regular veterinary checkups are non-negotiable for early detection and management of these recurring problems.
7. Dachshund
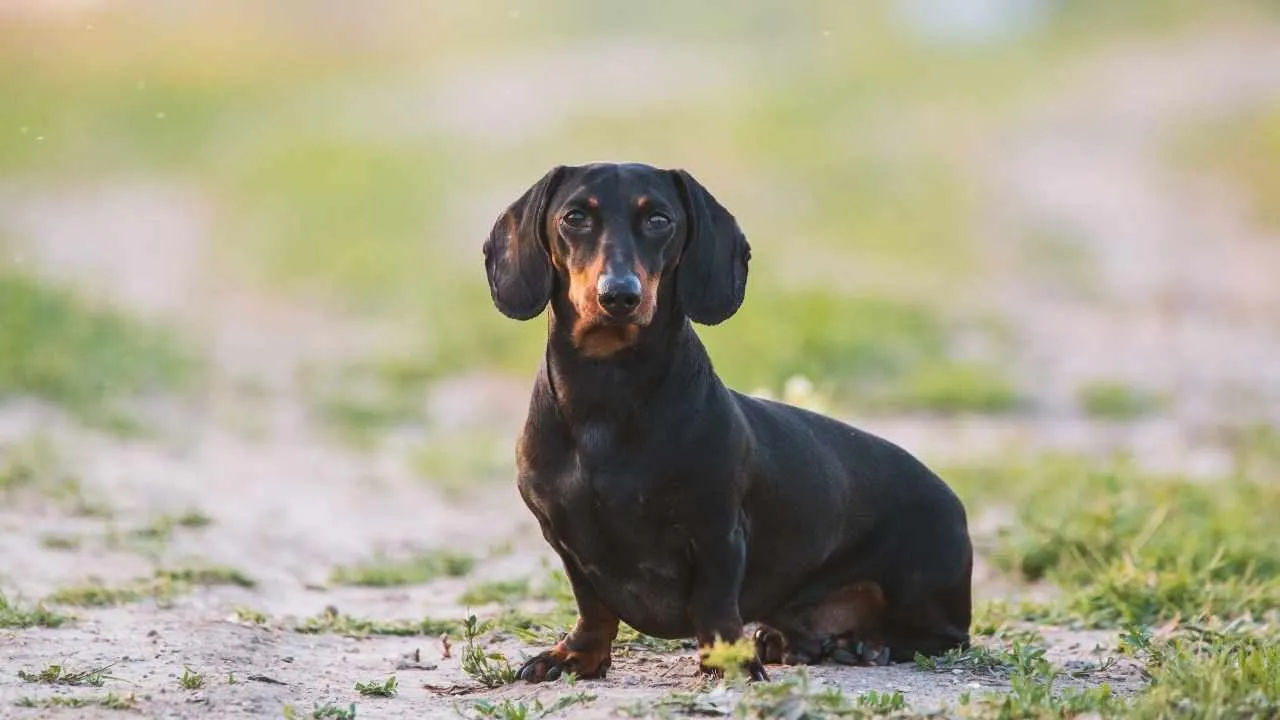

The dachshund’s long body and short legs make them instantly recognizable and entertaining to watch as they trots around. Yet this same structure places considerable stress on their spine, leaving them more vulnerable to mobility concerns than many other breeds.
Back and Spinal Concerns
One of the most significant risks for dachshunds is Intervertebral Disc Disease, where weakened discs can press on the spinal cord and cause pain or paralysis, as mentioned in the Kennel Club. Preventing spinal problems often comes down to managing weight and limiting high-impact activities like jumping off furniture or climbing stairs.

Weight and Oral Health
Obesity is another issue that quickly worsens existing back troubles while increasing the risk of diabetes and joint pain. Dental care also requires special attention, as their small mouths lead to crowded teeth. Owners should keep up with brushing, dental chews, and cleanings.
Supporting Long-Term Wellbeing
Helping this breed stay healthy means creating a lifestyle that avoids strain on their back while maintaining fitness. Some helpful strategies include:
Feeding balanced meals in controlled portions
Using ramps instead of stairs for easier access
Encouraging gentle, regular exercise over strenuous play
Conclusion
Awareness is the foundation of responsible ownership, especially when some breeds carry serious risks. From cardiac disorders to chronic breathing problems, breed-specific health issues can shorten lifespans and increase suffering.
Families who prioritize a healthy breed improve the odds of raising pets who thrive with energy and affection. Exploring the healthiest dog breeds ensures stronger immunity, fewer vet emergencies, and a smoother transition into family life.
Still, every dog’s health depends on attentive care, regular checkups, and daily mental stimulation. Choosing wisely means building a future where companionship is defined by joy, not medical hardship.


